Renal artery embolization
- PMID: 23204638
- PMCID: PMC3312178
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1296082
Renal artery embolization
Abstract
Renal artery embolization (RAE) is an effective minimally invasive alternative procedure for the treatment of a variety of conditions. Since the 1970s when RAE was first developed, technical advances and growing experience have expanded the indications to not only include treatment of conditions such as symptomatic hematuria and palliation for metastatic renal cancer, but also preoperative infarction of renal tumors, treatment of angiomyolipomas, vascular malformations, medical renal disease, and complications following renal transplantation. With the drastically improved morbidity associated with this technique in part due to the introduction of more precise embolic agents and smaller delivery catheters, RAE continues to gain popularity for various urologic conditions. The indications and techniques for renal artery embolization are reviewed in the following sections.
Keywords: Embolization; hemorrhage; interventional radiology; kidney; renal artery.
Figures



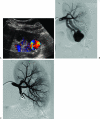
References
-
- Turini D, Nicita G, Fiorelli C, Selli C, Villari N. Selective transcatheter arterial embolization of renal carcinoma: an original technique. J Urol. 1976;116(4):419–421. - PubMed
-
- Kadir S, Marshall F F, White R I, Jr, Kaufman S L, Barth K H. Therapeutic embolization of the kidney with detachable silicone balloons. J Urol. 1983;129(1):11–13. - PubMed
-
- Hom D, Eiley D, Lumerman J H, Siegel D N, Goldfischer E R, Smith A D. Complete renal embolization as an alternative to nephrectomy. J Urol. 1999;161(1):24–27. - PubMed
-
- Ginat D T, Saad W E, Turba U C. Transcatheter renal artery embolization: clinical applications and techniques. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;12(4):224–239. - PubMed
-
- Takebayashi S, Hosaka M, Kubota Y, Ishizuka E, Iwasaki A, Matsubara S. Transarterial embolization and ablation of renal arteriovenous malformations: efficacy and damages in 30 patients with long-term followup. J Urol. 1998;159(3):696–701. - PubMed

