Collective epithelial and mesenchymal cell migration during gastrulation
- PMID: 23204916
- PMCID: PMC3394114
- DOI: 10.2174/138920212800793357
Collective epithelial and mesenchymal cell migration during gastrulation
Abstract
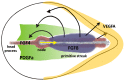
Gastrulation, the process that puts the three major germlayers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm in their correct topological position in the developing embryo, is characterised by extensive highly organised collective cell migration of epithelial and mesenchymal cells. We discuss current knowledge and insights in the mechanisms controlling these cell behaviours during gastrulation in the chick embryo. We discuss several ideas that have been proposed to explain the observed large scale vortex movements of epithelial cells in the epiblast during formation of the primitive streak. We review current insights in the control and execution of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) underlying the formation of the hypoblast and the ingression of the mesendoderm cells through the streak. We discuss the mechanisms by which the mesendoderm cells move, the nature and dynamics of the signals that guide these movements, as well as the interplay between signalling and movement that result in tissue patterning and morphogenesis. We argue that instructive cell-cell signaling and directed chemotactic movement responses to these signals are instrumental in the execution of all phases of gastrulation.
Keywords: Development; EMT; FGF signalling.; chemotaxis; chick embryo; ingression.
Figures
References
-
- Stern CD. In: Gastrulation, from cells to embryo's. Stern CD, editor. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2004.
-
- Chuai M, Dormann D, Weijer CJ. Imaging cell signalling and movement in development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009;20(8):947–955. - PubMed
-
- Eyal-Giladi H, Kochav S. From cleavage to primitive streak formation: a complementary normal table and a new look at the first stages of the development of the chick. I. General morphology. Dev. Biol. 1976;49(2):321–337. - PubMed
-
- Downie JR. The mechanism of chick blastoderm expansion. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1976;35(3):559–575. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
