Identification of pathogenesis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma by expression profiling
- PMID: 23205106
- PMCID: PMC3506695
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.810
Identification of pathogenesis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma by expression profiling
Abstract
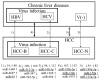
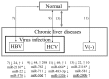
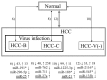
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors of the liver. Since postoperative recurrence and intrahepatic metastases occur frequently, the postoperative 5-year survival rate is low. To investigate the molecular mechanisms of HCC progression, mRNA as well as microRNA (miRNA) expression levels have been profiled in various studies. However, no previous study has comprehensively compared the expression of miRNAs in HCC patients with various clinical features using the tumor and surrounding non-tumor tissues and normal liver samples. In this study, we profiled the expression of miRNAs in tumor and non-tumor tissues from 40 HCC patients with heterogeneous pathogenesis and 6 surrounding non-tumor tissues from patients with metastatic liver cancer. To identify miRNAs specific to each disease state, we comprehensively compared the expression of miRNAs in various combinations. The results indicate that the expression of many known as well as novel miRNAs was altered in patients with the hepatitis C virus infection compared with those with the hepatitis B virus and without any virus infection. The following miRNAs were downregulated in the tumor and non-tumor tissues, and thus could serve as novel biomarkers for chronic liver diseases: miR-18b*, miR-296-5p, miR-557, miR-581, miR-625*, miR-1228, miR-1249 and miR-2116*. Similarly, miR-129*, miR-146b-3p and miR-448 are novel candidates for HCC biomarkers regardless of virus infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Profiles of serum microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223-3p serve as novel biomarkers for HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Jul;41(7):4513-9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3322-3. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24595450
-
Hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma at the miRNA level.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul 28;17(28):3353-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3353. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21876625 Free PMC article.
-
The exosome encapsulated microRNAs as circulating diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma with low alpha-fetoprotein.Int J Cancer. 2020 Nov 15;147(10):2934-2947. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33111. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32441313
-
Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma using expression data of independent datasets.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 15;8(1):9227. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27521-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29907753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targets and Signaling Pathways of microRNA-122 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 29;14(7):1380. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071380. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes derived from miR-1228 overexpressing bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells promote growth of gastric cancer cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 21;13(8):11808-11821. doi: 10.18632/aging.202878. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33883305 Free PMC article.
-
NEDD 4 binding protein 2-like 1 promotes cancer cell invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Virchows Arch. 2016 Aug;469(2):163-72. doi: 10.1007/s00428-016-1955-4. Epub 2016 May 16. Virchows Arch. 2016. PMID: 27184799
-
Hsa-miR-557 Inhibits Osteosarcoma Growth Through Targeting KRAS.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 11;12:789823. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.789823. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35087570 Free PMC article.
-
miR-144 reverses chemoresistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines by targeting Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Jul 15;8(7):2992-3002. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27508019 Free PMC article.
-
miR-144 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting E2F3.Tumour Biol. 2014 Nov;35(11):10759-64. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2017-7. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25073510
References
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Soini Y, Chia SC, Bennett WP, et al. An aflatoxin-associated mutational hotspot at codon 249 in the p53 tumor suppressor gene occurs in hepatocellular carcinomas from Mexico. Carcinogenesis. 1996;17:1007–1012. - PubMed
-
- Boffetta P, Matisane L, Mundt KA, Dell LD. Meta-analysis of studies of occupational exposure to vinyl chloride in relation to cancer mortality. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2003;29:220–229. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
