Adjuvant combined systemic chemotherapy and intraperitoneal chemotherapy for locally advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 23205128
- PMCID: PMC3506743
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.914
Adjuvant combined systemic chemotherapy and intraperitoneal chemotherapy for locally advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
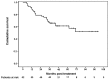
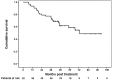
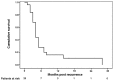
The optimal adjuvant treatment modality for gastric cancer has not been well defined. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and feasibility of adjuvant combined systemic and intraperitoneal chemotherapy (ACSIP) in high-risk patients with locally advanced gastric cancer. Between June 2003 and December 2008, 62 eligible patients with serosa-infiltrating and/or node-positive gastric cancer following curative gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy received ACSIP, consisting of intravenous oxaliplatin 85 mg/m(2) on day 1 followed by leucovorin (LV) 200 mg/m(2) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) 450 mg/m(2) on days 1-3, intraperitoneal 5-FU 600 mg/m(2) on days 4-5 and cisplatin (CDDP) 40 mg/m(2) on day 5. Survival rates, the sites of first treatment failure and safety were analyzed. At a median follow-up of 45 months (range 7-101), the 3-year disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) rates were 66.1 and 74.2%, respectively. Initial peritoneal and hepatic failures were found in 6 (24.0%) and 3 (12.0%) of the 25 patients with recurrence, respectively. Neutropenia, gastrointestinal side effects and peripheral neuropathy were the most common grade 3-4 toxicities; however, they were all infrequent and manageable. No serious surgical complications or treatment-related mortality was observed. The results of this study indicate that ACSIP is effective and feasible for locally advanced gastric cancer with encouraging survival rates and possibly decreased peritoneal and hepatic recurrences. The benefits of this promising combined adjuvant treatment modality warrant further studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A phase II trial of neoadjuvant cisplatin-fluorouracil followed by postoperative intraperitoneal floxuridine-leucovorin in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer.Ann Oncol. 2006 Sep;17(9):1404-11. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdl133. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Ann Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16788003 Clinical Trial.
-
[Safety and efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy with oxaliplatin and S-1 for patients with locally advanced gastric cancer after D2 lymph nodes dissection].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Feb 25;24(2):145-152. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20201016-00561. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33508920 Chinese.
-
Effect of Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Perfusion Chemotherapy in Combination with Intravenous Chemotherapy as Postoperative Adjuvant Therapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer.Hepatogastroenterology. 2014 Jun;61(132):972-7. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 26158151
-
Combined intravenous and intraperitoneal chemotherapy with fluorouracil + leucovorin vs fluorouracil + levamisole for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 1998 Apr;77(8):1349-54. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.225. Br J Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9579845 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chemotherapy Options for Locally Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;17(5):809. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050809. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intraperitoneal chemotherapy for gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis.Gastric Cancer. 2017 Mar;20(Suppl 1):111-121. doi: 10.1007/s10120-016-0662-9. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Gastric Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27803990 Review.
-
Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in prevention of gastric cancer metachronous peritoneal metastases: a systematic review.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Apr;12(Suppl 1):S5-S17. doi: 10.21037/jgo-20-129. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33968422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DCF intraperitoneal and intravenous dual chemotherapy regimen for advanced gastric cancer: A feasibility study.Oncol Lett. 2015 Jan;9(1):491-497. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2651. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25436015 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Adjuvant Systemic Chemotherapy Combined with Radical Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer Treatment.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2020 Sep;11(3):337-343. doi: 10.1007/s13193-020-01102-w. Epub 2020 May 19. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33013107 Free PMC article.
-
What make differences in the outcome of adjuvant treatments for resected gastric cancer?World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 7;20(33):11567-73. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11567. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25206264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhao P, Dai M, Chen W, Li N. Cancer trends in China. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010;40:281–285. - PubMed
-
- Wu CW, Lo SS, Shen KH, et al. Incidence and factors associated with recurrence patterns after intended curative surgery for gastric cancer. World J Surg. 2003;27:153–158. - PubMed
-
- Sugarbaker PH, Yu W, Yonemura Y. Gastrectomy, peritonectomy, and perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy: the evolution of treatment strategies for advanced gastric cancer. Semin Surg Oncol. 2003;21:233–248. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, et al. Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:725–730. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:11–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
