Effect of Biologic Agents on Non-PASI Outcomes in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses
- PMID: 23205332
- PMCID: PMC3510417
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-012-0009-3
Effect of Biologic Agents on Non-PASI Outcomes in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of this review was to conduct a systematic review with meta-analysis and Bayesian mixed treatment comparisons (MTC) evaluating the impact of biologics on non-Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) health outcomes in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
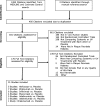
Methods: MEDLINE and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from 1966 to May 2009. Citations were screened for randomized, controlled trials of biologics versus either placebo or each other in adults with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis and reported any of several outcomes. Traditional and Bayesian MTC meta-analyses were conducted for each endpoint using either a random- or fixed-effect model where appropriate.
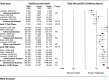
Results: Thirty-eight studies met eligibility criteria. All biologics showed significant improvement in achieving a good response on the static physician's global assessment (PGA) versus placebo while, in the MTC, differences were noted between individual drugs. In achieving a good response on the dynamic PGA, all biologics showed significant improvements over placebo, while the MTC showed significant improvements with the anti-interleukins versus anti-T cells. Relative to placebo, antitumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents and anti-interleukins showed significant improvements in the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). Compared with placebo, the anti-TNF agents showed significant improvements in both 36-item Medical Outcomes Study Short-Form General Health Survey (SF-36) mental and physical component scores, while anti-T cell agents showed no improvements. The MTC showed no differences between any biologics for either the DLQI or SF-36.
Conclusion: Individual biologics and classes showed consistent benefits across non-PASI health outcomes in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis while MTC meta-analyses suggested that some differences exist.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
