Decreased health-related quality of life in women with breast cancer is associated with poor sleep
- PMID: 23205513
- PMCID: PMC3594390
- DOI: 10.1080/15402002.2012.660589
Decreased health-related quality of life in women with breast cancer is associated with poor sleep
Abstract
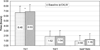
This study examined the longitudinal relation between health-related quality of life (HR-QOL) and subjective and objective sleep quality in 166 women with newly diagnosed Stage-1 through Stage-3 breast cancer, who were scheduled to receive ≥ 4 cycles of adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy. HR-QOL was assessed with the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item Short Form, Physical Component Scale (PCS), and Mental Component Scale (MCS) scores; subjective sleep was assessed with the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; and objective sleep was measured with actigraphy. Data were collected before starting chemotherapy and during the last week of Cycle 4 of chemotherapy. Patients reported poor HR-QOL and poor sleep quality before and during chemotherapy. Short sleep time and long naps were recorded at both time points. The MCS score was related to reports of poor sleep, but not to recorded sleep; worse PCS scores were associated with reports of poor sleep and less recorded naptime, suggesting sleep plays an important role in cancer patients' HR-QOL.
Figures

References
-
- Ancoli-Israel S, Cole R, Alessi CA, Chambers M, Moorcroft WH, Pollak C. The role of actigraphy in the study of sleep and circadian rhythms. Sleep. 2003;26:342–392. - PubMed
-
- Beck SL, Schwartz AL, Towsley G, Dudley W, Barsevick A. Psychometric evaluation of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index in cancer patients. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2004;27:140–148. - PubMed
-
- Berger AM, Sankaranarayanan J, Watanabe-Galloway S. Current methodological approaches to the study of sleep disturbances and quality of life in adults with cancer: a systematic review. Psychooncology. 2007;16:401–420. - PubMed
-
- Bower JE, Ganz PA, Desmond KA, Rowland JH, Meyerowitz BE, Belin TR. Fatigue in breast cancer survivors: occurrence, correlates, and impact on quality of life. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000;18:743–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
