Resistance, aerobic, and combination training on vascular function in overweight and obese adults
- PMID: 23205751
- PMCID: PMC8108867
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00700.x
Resistance, aerobic, and combination training on vascular function in overweight and obese adults
Abstract
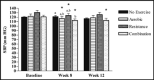
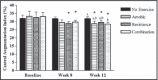
The authors investigated the effects of moderate-intensity resistance, aerobic, or combined exercise on blood pressure and arterial stiffness in overweight and obese individuals compared with no exercise. Participants were randomized to 4 groups: control, aerobic, resistance, and combination. Assessments were made at baseline, week 8, and week 12. In participant-designated responders, those in the intervention groups who had improved levels of systolic blood pressure (SBP) or augmentation index (AI), we observed a significant decrease of SBP in aerobic (-4%, P=.027), resistance (-5.1%, P=.04), and combination groups (-6.3%, P=.000) at week 8 and in the combination group (-6.3%, P=.005) at week 12, compared with baseline. AI was significantly lower at week 12 in the aerobic (-12%, P=.047), resistance (-9.5%, P=.036), and combination (-12.7%, P=.003) groups compared with baseline, as well as in the combination group (-10.7%, P=.047) compared with the control group. We did not observe significant changes in SBP, DBP, or AI between the interventions when assessing the entire cohort, although there were significant improvements in a subgroup of responders. Thus, some but not all overweight and obese individuals can improve blood pressure and arterial stiffness by participating in regular combination exercise, decreasing the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare . Australia’s Health, 2006. Canberra, ACT: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare; 2006.
-
- Barr ELM, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ, et al. AusDiab 2005: The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study. Melbourne, Vic., Australia: International Diabetes Institute; 2006.
-
- Wassertheil‐Smoller S, Anderson G, Psaty BM, et al. Hypertension and its treatment in postmenopausal women: baseline data from the women’s health initiative. Hypertension. 2000;36:780–789. - PubMed
-
- Fagard RH, Cornelissen VA. Effect of exercise on blood pressure control in hypertensive patients. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007;14:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Katzmarzyk PT, Leon AS, Wilmore JH, et al. Targeting the metabolic syndrome with exercise: evidence from the HERITAGE family study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003;35:1703–1709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

