Bench-to-bedside review: Clinical experience with the endotoxin activity assay
- PMID: 23206992
- PMCID: PMC3672550
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11495
Bench-to-bedside review: Clinical experience with the endotoxin activity assay
Abstract
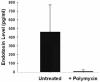
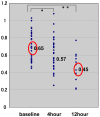
Endotoxin detection in human patients has been a difficult challenge, in part due to the fact that the conserved active portion of the molecule (lipid A) is a relatively small epitope only amenable to binding by a single ligand at any one instance and low levels (pg/ml) are capable of stimulating the immune system. The endotoxin activity assay, a bioassay based on neutrophil activation by complement opsonized immune complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), has allowed the specific detection of the lipid A epitope of LPS in a rapid whole blood assay format. This review summarizes diagnostic studies utilizing the endotoxin activity assay in a variety of hospital patient populations in whom endotoxin is postulated to play a significant role in disease etiology. These include ICU patients at risk of developing 'sepsis syndrome', abdominal and cardiovascular surgery patients and patients with serious traumatic injury. Significant features of these studies include the high negative predictive value of the assay (98.6%) for rule out of Gram-negative infection, ability to risk stratify patients progressing to severe sepsis (odds ratio 3.0) and evidence of LPS release in patients with gut hypoperfusion. Preliminary studies have successfully combined the assay with anti-LPS removal strategies to prospectively identify patients who might benefit from this therapy with early evidence of clinical benefit.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endotoxin Activity Assay for the Detection of Whole Blood Endotoxemia in Critically Ill Patients.J Vis Exp. 2019 Jun 24;(148). doi: 10.3791/58507. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31282890
-
A true theranostic approach to medicine: towards tandem sensor detection and removal of endotoxin in blood.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 May 15;67:3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25067837
-
A rapid assay of endotoxin in whole blood using autologous neutrophil dependent chemiluminescence.J Immunol Methods. 1998 Mar 15;212(2):169-85. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(98)00003-9. J Immunol Methods. 1998. PMID: 9672205
-
Endotoxins and other sepsis triggers.Contrib Nephrol. 2010;167:14-24. doi: 10.1159/000315915. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Contrib Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20519895 Review.
-
Therapeutic Rationale for Endotoxin Removal with Polymyxin B Immobilized Fiber Column (PMX) for Septic Shock.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 23;22(4):2228. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042228. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic endotoxin activity correlates with clot formation: an observational study in patients with early systemic inflammation and sepsis.Crit Care. 2013 Sep 11;17(5):R198. doi: 10.1186/cc12892. Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 24025340 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin Elimination in Patients with Septic Shock: An Observation Study.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2015 Dec;63(6):475-83. doi: 10.1007/s00005-015-0348-8. Epub 2015 Jun 21. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2015. PMID: 26093653 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin removal therapy with Polymyxin B immobilized fiber column as a COVID-19-bedside strategy protocol for endotoxic shock.Front Nephrol. 2022 Aug 3;2:847305. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2022.847305. eCollection 2022. Front Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 37675016 Free PMC article.
-
Lubiprostone improves intestinal permeability in humans, a novel therapy for the leaky gut: A prospective randomized pilot study in healthy volunteers.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 14;12(4):e0175626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175626. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28410406 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic value of endotoxin activity assay in patients with severe sepsis after cardiac surgery.J Inflamm (Lond). 2013 Mar 6;10(1):8. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-10-8. J Inflamm (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23510603 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

