A molecular link between miRISCs and deadenylases provides new insight into the mechanism of gene silencing by microRNAs
- PMID: 23209154
- PMCID: PMC3504443
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012328
A molecular link between miRISCs and deadenylases provides new insight into the mechanism of gene silencing by microRNAs
Abstract
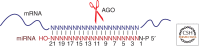
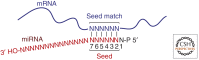
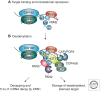
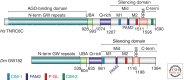
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a large family of endogenous noncoding RNAs that, together with the Argonaute family of proteins (AGOs), silence the expression of complementary mRNA targets posttranscriptionally. Perfectly complementary targets are cleaved within the base-paired region by catalytically active AGOs. In the case of partially complementary targets, however, AGOs are insufficient for silencing and need to recruit a protein of the GW182 family. GW182 proteins induce translational repression, mRNA deadenylation and exonucleolytic target degradation. Recent work has revealed a direct molecular link between GW182 proteins and cellular deadenylase complexes. These findings shed light on how miRNAs bring about target mRNA degradation and promise to further our understanding of the mechanism of miRNA-mediated repression.
Figures
References
-
- Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K, Holtz J, Eachus R, Pasquinelli AE 2005. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell 122: 553–563 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
