The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin counteracts stroke in the normal and diabetic mouse brain: a comparison with glimepiride
- PMID: 23209191
- PMCID: PMC3609599
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0988
The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin counteracts stroke in the normal and diabetic mouse brain: a comparison with glimepiride
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes is a strong risk factor for stroke. Linagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor in clinical use against type 2 diabetes. The aim of this study was to determine the potential antistroke efficacy of linagliptin in type 2 diabetic mice. To understand whether efficacy was mediated by glycemia regulation, a comparison with the sulfonylurea glimepiride was done. To determine whether linagliptin-mediated efficacy was dependent on a diabetic background, experiments in nondiabetic mice were performed. Type 2 diabetes was induced by feeding the mice a high-fat diet for 32 weeks. Mice were treated with linagliptin/glimepiride for 7 weeks. Stroke was induced at 4 weeks into the treatment by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Blood DPP-4 activity, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) levels, glucose, body weight, and food intake were assessed throughout the experiments. Ischemic brain damage was measured by determining stroke volume and by stereologic quantifications of surviving neurons in the striatum/cortex. We show pronounced antistroke efficacy of linagliptin in type 2 diabetic and normal mice, whereas glimepiride proved efficacious against stroke in normal mice only. These results indicate a linagliptin-mediated neuroprotection that is glucose-independent and likely involves GLP-1. The findings may provide an impetus for the development of DPP-4 inhibitors for the prevention and treatment of stroke in diabetic patients.
Figures


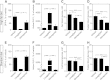

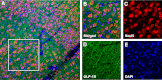
Comment in
-
DPP-4 inhibition and neuroprotection: do mechanisms matter?Diabetes. 2013 Apr;62(4):1029-31. doi: 10.2337/db12-1794. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23520281 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001;414:782–787 - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2003;348:383–393 - PubMed
-
- Sander D, Kearney MT. Reducing the risk of stroke in type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological and therapeutic perspectives. J Neurol 2009;256:1603–1619 - PubMed
-
- Harmsen P, Lappas G, Rosengren A, Wilhelmsen L. Long-term risk factors for stroke: twenty-eight years of follow-up of 7457 middle-aged men in Göteborg, Sweden. Stroke 2006;37:1663–1667 - PubMed
-
- Haratz S, Tanne D. Diabetes, hyperglycemia and the management of cerebrovascular disease. Curr Opin Neurol 2011;24:81–88 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

