Reconstructing mammalian sleep dynamics with data assimilation
- PMID: 23209396
- PMCID: PMC3510073
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002788
Reconstructing mammalian sleep dynamics with data assimilation
Abstract
Data assimilation is a valuable tool in the study of any complex system, where measurements are incomplete, uncertain, or both. It enables the user to take advantage of all available information including experimental measurements and short-term model forecasts of a system. Although data assimilation has been used to study other biological systems, the study of the sleep-wake regulatory network has yet to benefit from this toolset. We present a data assimilation framework based on the unscented Kalman filter (UKF) for combining sparse measurements together with a relatively high-dimensional nonlinear computational model to estimate the state of a model of the sleep-wake regulatory system. We demonstrate with simulation studies that a few noisy variables can be used to accurately reconstruct the remaining hidden variables. We introduce a metric for ranking relative partial observability of computational models, within the UKF framework, that allows us to choose the optimal variables for measurement and also provides a methodology for optimizing framework parameters such as UKF covariance inflation. In addition, we demonstrate a parameter estimation method that allows us to track non-stationary model parameters and accommodate slow dynamics not included in the UKF filter model. Finally, we show that we can even use observed discretized sleep-state, which is not one of the model variables, to reconstruct model state and estimate unknown parameters. Sleep is implicated in many neurological disorders from epilepsy to schizophrenia, but simultaneous observation of the many brain components that regulate this behavior is difficult. We anticipate that this data assimilation framework will enable better understanding of the detailed interactions governing sleep and wake behavior and provide for better, more targeted, therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


 (blue) were passed to the unscented kalman filter (UKF) framework to track and reconstruct all other variables. Shown are the firing rates for the Wake-active (LC), NREM-active (VLPO), and REM-active (LDT/PPT) cell groups, along with thalamic noise
(blue) were passed to the unscented kalman filter (UKF) framework to track and reconstruct all other variables. Shown are the firing rates for the Wake-active (LC), NREM-active (VLPO), and REM-active (LDT/PPT) cell groups, along with thalamic noise  . The framework was given the same parameters used to generate the original data. In both A and B the same data was tracked with model initial conditions chosen randomly. After a transient period, reconstructed (red) Wake and NREM dynamics are close to true (black) dynamics. Without
. The framework was given the same parameters used to generate the original data. In both A and B the same data was tracked with model initial conditions chosen randomly. After a transient period, reconstructed (red) Wake and NREM dynamics are close to true (black) dynamics. Without  optimization the dynamics of
optimization the dynamics of  are essentially ignored. After
are essentially ignored. After  optimization at least some of the stochastic
optimization at least some of the stochastic  dynamics - those that measurably affect the dynamics of
dynamics - those that measurably affect the dynamics of  - are reconstructed and reconstruction of REM dynamics is improved.
- are reconstructed and reconstruction of REM dynamics is improved.
 for the DB model with no thalamic noise and default values of
for the DB model with no thalamic noise and default values of  .
.  is an empirical measure of how well variable
is an empirical measure of how well variable  is reconstructed from measurement of variable
is reconstructed from measurement of variable  .
.  with perfect reconstruction being 1. Here
with perfect reconstruction being 1. Here  was computed using 12 hours of data. From the
was computed using 12 hours of data. From the  matrix, we observe that
matrix, we observe that  (row) is poorly observed - poorly reconstructed - from most variables, although its measurement (column) yields good reconstruction of almost all other variables.
(row) is poorly observed - poorly reconstructed - from most variables, although its measurement (column) yields good reconstruction of almost all other variables.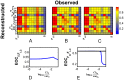
 can be used to guide optimization of the covariance inflater
can be used to guide optimization of the covariance inflater  : Poorly observed variables across their rows - low
: Poorly observed variables across their rows - low  - should have decreased
- should have decreased  . Variables whose measurement yields poor reconstruction columnwise- low
. Variables whose measurement yields poor reconstruction columnwise- low  - should have increased
- should have increased  . Algorithmically, we iteratively adjust
. Algorithmically, we iteratively adjust  for the variable
for the variable  with the overall lowest mean row or column. In A–C are shown the
with the overall lowest mean row or column. In A–C are shown the  matrix after each optimization iteration for the full DB model with thalamic noise. A)
matrix after each optimization iteration for the full DB model with thalamic noise. A)  computed with default values for
computed with default values for  , i.e.
, i.e.  . Note that the lowest mean row/column corresponds to the measurement of
. Note that the lowest mean row/column corresponds to the measurement of  , therefore we optimize
, therefore we optimize  first. B)
first. B)  after optimization of
after optimization of  . C)
. C)  after optimizing
after optimizing  . Shown are
. Shown are  as a function of D)
as a function of D)  for optimization step between A and B and E)
for optimization step between A and B and E)  for optimization steps between B and C. Optimal values of
for optimization steps between B and C. Optimal values of  are chosen from the peaks of these plots.
are chosen from the peaks of these plots.
 to the true value. B) Trajectories for the short model generated (magenta), reconstructed (red), and true (black)
to the true value. B) Trajectories for the short model generated (magenta), reconstructed (red), and true (black)  dynamics for different periods of the convergence of
dynamics for different periods of the convergence of  . Note that initially, for
. Note that initially, for  significantly different than the true value, the short trajectories diverge quickly from the reconstructed values, and the reconstructed values of of
significantly different than the true value, the short trajectories diverge quickly from the reconstructed values, and the reconstructed values of of  are different from the true values. When
are different from the true values. When  approaches the true value, both short model-generated and reconstructed trajectories approach the true values. C) Reconstruction metric
approaches the true value, both short model-generated and reconstructed trajectories approach the true values. C) Reconstruction metric  computed for each data assimilation window for three of the variables. As a reference point, the reconstruction metric for the original noisy observation of
computed for each data assimilation window for three of the variables. As a reference point, the reconstruction metric for the original noisy observation of  is shown in blue. Note that although the parameter estimation essentially optimizes short model generated forecasts, it has the effect of optimizing hidden variable reconstruction.
is shown in blue. Note that although the parameter estimation essentially optimizes short model generated forecasts, it has the effect of optimizing hidden variable reconstruction.
 and
and  from the full FBFD model were assimilated with a version of the DB model that represented input from the SCN as a quasi-static parameter
from the full FBFD model were assimilated with a version of the DB model that represented input from the SCN as a quasi-static parameter  whose value was estimated and tracked in 80% overlapping half hour windows. SCN activity imposes circadian and light-driven dynamics that modulate sleep-wake cycles and prevalence of either sleep or wake activity. A) Short excerpts of reconstructed dynamics for various phases of the circadian cycle. B) Estimated (magenta) and true (black) value of the tracked parameter
whose value was estimated and tracked in 80% overlapping half hour windows. SCN activity imposes circadian and light-driven dynamics that modulate sleep-wake cycles and prevalence of either sleep or wake activity. A) Short excerpts of reconstructed dynamics for various phases of the circadian cycle. B) Estimated (magenta) and true (black) value of the tracked parameter  . Note that the tracked value is an estimate, with inherent smoothing on the time scale of a half hour, and therefore does not reconstruct all of the detailed dynamics of the true value which oscillates due to the interplay between the core sleep-wake regulatory cell groups and the SCN. C) Normalized reconstruction error for various variables. As a reference, the reconstruction error for the noisy
. Note that the tracked value is an estimate, with inherent smoothing on the time scale of a half hour, and therefore does not reconstruct all of the detailed dynamics of the true value which oscillates due to the interplay between the core sleep-wake regulatory cell groups and the SCN. C) Normalized reconstruction error for various variables. As a reference, the reconstruction error for the noisy  measurement is shown in blue. The reconstruction of unobserved variables
measurement is shown in blue. The reconstruction of unobserved variables  and homeostatic sleep drive
and homeostatic sleep drive  is quite good as indicated by small
is quite good as indicated by small  values.
values.
 ,
,  , and
, and  , and their variances. We use the UKF to reconstruct the full variable state space from these observations. A) Probability distributions of firing rates for
, and their variances. We use the UKF to reconstruct the full variable state space from these observations. A) Probability distributions of firing rates for  ,
,  and
and  during Wake (black), NREM (red), and REM (blue). These firing rates were generated from the filter-model. B) Hypnogram of observed SOV for a 1 hour time series, with colors to match (A). C) Reconstructed (red) and true (black) traces for
during Wake (black), NREM (red), and REM (blue). These firing rates were generated from the filter-model. B) Hypnogram of observed SOV for a 1 hour time series, with colors to match (A). C) Reconstructed (red) and true (black) traces for  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  . The inferred observation for
. The inferred observation for  is also shown (blue). After a transient period, the reconstruction converges to the true value, even for the homeostatic drive variable
is also shown (blue). After a transient period, the reconstruction converges to the true value, even for the homeostatic drive variable  which was not observed. However, details of the dynamics that are not accounted for by the state-of-vigilance (SOV) such as brief awakenings and transitions into and out of NREM are not reconstructed well.
which was not observed. However, details of the dynamics that are not accounted for by the state-of-vigilance (SOV) such as brief awakenings and transitions into and out of NREM are not reconstructed well.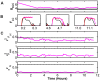
 dynamics for different periods of the convergence of
dynamics for different periods of the convergence of  . C) Reconstruction metric
. C) Reconstruction metric  computed for each data assimilation window for three of the variables. Horizontal dashed lines correspond to
computed for each data assimilation window for three of the variables. Horizontal dashed lines correspond to  computed from the state-conditioned discrete map used to translate the SOV to model space. Note that once the parameter is optimized, the UKF reconstruction far outperforms the observation map.
computed from the state-conditioned discrete map used to translate the SOV to model space. Note that once the parameter is optimized, the UKF reconstruction far outperforms the observation map.References
-
- Saper CB, Scammel TE, Lu J (2005) Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms. Nature 437: 1257–63. - PubMed
-
- Tamakawa Y, Karashima A, Koyoma Y, Katayama N, Nakao M (2006) A quartet neural system model orchestrating sleep and wakefulness mechanisms. J Neurophysiol 95: 2055–69. - PubMed
-
- Diniz Behn CG, Booth V (2010) Simulating microinjection experiments in a novel model of the rat sleep-wake regulatory network. J Neurophysiol 103: 1937–1953. - PubMed
-
- Phillips JK, Robinson PA (2007) A quantitative model of sleep-wake dynamics based on the physiology of the brainstem ascending arousal system. J Biological Rhythms 22: 167–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

