Neutrophil-derived IL-1β is sufficient for abscess formation in immunity against Staphylococcus aureus in mice
- PMID: 23209417
- PMCID: PMC3510260
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003047
Neutrophil-derived IL-1β is sufficient for abscess formation in immunity against Staphylococcus aureus in mice
Abstract
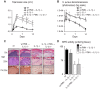
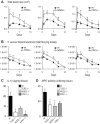
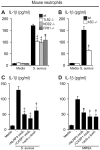
Neutrophil abscess formation is critical in innate immunity against many pathogens. Here, the mechanism of neutrophil abscess formation was investigated using a mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus cutaneous infection. Gene expression analysis and in vivo multispectral noninvasive imaging during the S. aureus infection revealed a strong functional and temporal association between neutrophil recruitment and IL-1β/IL-1R activation. Unexpectedly, neutrophils but not monocytes/macrophages or other MHCII-expressing antigen presenting cells were the predominant source of IL-1β at the site of infection. Furthermore, neutrophil-derived IL-1β was essential for host defense since adoptive transfer of IL-1β-expressing neutrophils was sufficient to restore the impaired neutrophil abscess formation in S. aureus-infected IL-1β-deficient mice. S. aureus-induced IL-1β production by neutrophils required TLR2, NOD2, FPR1 and the ASC/NLRP3 inflammasome in an α-toxin-dependent mechanism. Taken together, IL-1β and neutrophil abscess formation during an infection are functionally, temporally and spatially linked as a consequence of direct IL-1β production by neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Borregaard N (2010) Neutrophils, from marrow to microbes. Immunity 33: 657–670 S1074-7613(10)00417-6 [pii];10.1016/j.immuni.2010.11.011 [doi]. - PubMed
-
- Miller LS, O'Connell RM, Gutierrez MA, Pietras EM, Shahangian A, et al. (2006) MyD88 mediates neutrophil recruitment initiated by IL-1R but not TLR2 activation in immunity against Staphylococcus aureus . Immunity 24: 79–91. - PubMed
-
- Daum RS (2007) Clinical practice. Skin and soft-tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . N Engl J Med 357: 380–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

