Induced resistance by a long-chain bacterial volatile: elicitation of plant systemic defense by a C13 volatile produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa
- PMID: 23209558
- PMCID: PMC3509098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048744
Induced resistance by a long-chain bacterial volatile: elicitation of plant systemic defense by a C13 volatile produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa
Abstract
Background: Some strains of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) elicit induced systemic resistance (ISR) by emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) including short chain alcohols, acetoin, and 2,3-butanediol. The objective of this study was to evaluate whether species-specific VOCs from PGPR strain Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 can promote growth and induce resistance in Arabidopsis.
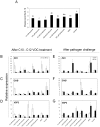
Methodology/principal findings: The efficacy of induction was strain-specific, with stronger protection against Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola ES4326 in plants exposed to VOCs from P. polymyxa E681 versus Arabidopsis plants exposed to VOCs from a reference strain Bacillus subtilis GB03, which was previously shown to elicit ISR and plant growth promotion. VOC emissions released from E681 primed transcriptional expression of the salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, and ethylene signaling marker genes PR1, ChiB, and VSP2, respectively. In addition, strain E681 produced more than thirty low molecular-weight VOCs, of which tridecane was only produced by E681 and not found in GB03 or IN937a volatile blends. These strain-specific VOCs induced PR1 and VSP2 genes.
Conclusions/significance: These results provide new insight into the existence of a long chain VOC signaling molecule produced by P. polymyxa that can serve as a bacterial trigger of induced systemic resistance in planta.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kloepper J, Metting F Jr. (1992) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as biological control agents. Soil microbial ecology: applications in agricultural and environmental management: 255–274.
-
- Ryu CM, Murphy JF, Mysore KS, Kloepper JW (2004) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria systemically protect Arabidopsis thaliana against Cucumber mosaic virus by a salicylic acid and NPR1-independent and jasmonic acid-dependent signaling pathway. Plant J 39: 381–392. - PubMed
-
- Ryu CM, Kim J, Choi O, Kim SH, Park CS (2006) Improvement of biological control capacity of Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 by seed pelleting on sesame. Biol Control 39: 282–289.
-
- Van Loon L, Bakker P, Pieterse C (1998) Systemic resistance induced by rhizosphere bacteria. Annu Rev Phytopathol 36: 453–483. - PubMed
-
- Kloepper JW, Ryu CM, Zhang S (2004) Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 94: 1259–1266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

