Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived models to investigate human cytomegalovirus infection in neural cells
- PMID: 23209593
- PMCID: PMC3507916
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049700
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived models to investigate human cytomegalovirus infection in neural cells
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(1). doi:10.1371/annotation/ea66e8f1-9f80-422f-8836-308a4cdc8ae4
Abstract
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection is one of the leading prenatal causes of congenital mental retardation and deformities world-wide. Access to cultured human neuronal lineages, necessary to understand the species specific pathogenic effects of HCMV, has been limited by difficulties in sustaining primary human neuronal cultures. Human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells now provide an opportunity for such research. We derived iPS cells from human adult fibroblasts and induced neural lineages to investigate their susceptibility to infection with HCMV strain Ad169. Analysis of iPS cells, iPS-derived neural stem cells (NSCs), neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and neurons suggests that (i) iPS cells are not permissive to HCMV infection, i.e., they do not permit a full viral replication cycle; (ii) Neural stem cells have impaired differentiation when infected by HCMV; (iii) NPCs are fully permissive for HCMV infection; altered expression of genes related to neural metabolism or neuronal differentiation is also observed; (iv) most iPS-derived neurons are not permissive to HCMV infection; and (v) infected neurons have impaired calcium influx in response to glutamate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
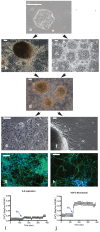
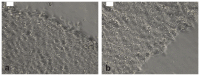


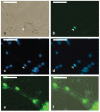
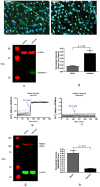
References
-
- Nelson CT, Demmler GJ (1997) Cytomegalovirus infection in the pregnant mother, fetus, and newborn infant. Clin Perinatol 24: 151–160. - PubMed
-
- Kosugi I, Kawasaki H, Tsuchida T, Tsutsui Y (2005) Cytomegalovirus infection inhibits the expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the developing mouse hippocampus and primary neuronal cultures. Acta Neuropathol 109: 475–482. - PubMed
-
- Kashiwai A, Kawamura N, Kadota C, Tsutsui Y (1992) Susceptibility of mouse embryo to murine cytomegalovirus infection in early and mid-gestation stages. Arch Virol 127: 37–48. - PubMed
-
- Neighbour PA (1978) Studies on the susceptibility of the mouse preimplantation embryo to infection with cytomegalovirus. J Reprod Fertil 54: 15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

