The delay in the development of experimental colitis from isomaltosyloligosaccharides in rats is dependent on the degree of polymerization
- PMID: 23209802
- PMCID: PMC3510184
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050658
The delay in the development of experimental colitis from isomaltosyloligosaccharides in rats is dependent on the degree of polymerization
Abstract
Background: Isomaltosyloligosaccharides (IMO) and dextran (Dex) are hardly digestible in the small intestine and thus influence the luminal environment and affect the maintenance of health. There is wide variation in the degree of polymerization (DP) in Dex and IMO (short-sized IMO, S-IMO; long-sized IMO, L-IMO), and the physiological influence of these compounds may be dependent on their DP.
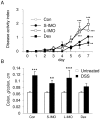
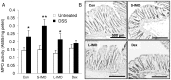
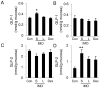
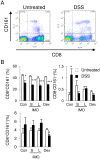
Methodology/principal findings: Five-week-old male Wistar rats were given a semi-purified diet with or without 30 g/kg diet of the S-IMO (DP = 3.3), L-IMO (DP = 8.4), or Dex (DP = 1230) for two weeks. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) was administered to the rats for one week to induce experimental colitis. We evaluated the clinical symptoms during the DSS treatment period by scoring the body weight loss, stool consistency, and rectal bleeding. The development of colitis induced by DSS was delayed in the rats fed S-IMO and Dex diets. The DSS treatment promoted an accumulation of neutrophils in the colonic mucosa in the rats fed the control, S-IMO, and L-IMO diets, as assessed by a measurement of myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. In contrast, no increase in MPO activity was observed in the Dex-diet-fed rats even with DSS treatment. Immune cell populations in peripheral blood were also modified by the DP of ingested saccharides. Dietary S-IMO increased the concentration of n-butyric acid in the cecal contents and the levels of glucagon-like peptide-2 in the colonic mucosa.
Conclusion/significance: Our study provided evidence that the physiological effects of α-glucosaccharides on colitis depend on their DP, linkage type, and digestibility.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

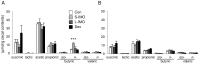
References
-
- Chen HL, Lu YH, Lin JJ, Ko LY (2001) Effects of isomalto-oligosaccharides on bowel functions and indicators of nutritional status in constipated elderly men. J Am Coll Nutr 20: 44–49. - PubMed
-
- Ketabi A, Dieleman LA, Ganzle MG (2011) Influence of isomalto-oligosaccharides on intestinal microbiota in rats. J Appl Microbiol 110: 1297–1306. - PubMed
-
- Ito H, Takemura N, Sonoyama K, Kawagishi H, Topping DL, et al. (2011) Degree of polymerization of inulin-type fructans differentially affects number of lactic acid bacteria, intestinal immune functions, and immunoglobulin A secretion in the rat cecum. J Agric Food Chem 59: 5771–5778. - PubMed
-
- Mizubuchi H, Yajima T, Aoi N, Tomita T, Yoshikai Y (2005) Isomalto-oligosaccharides polarize Th1-like responses in intestinal and systemic immunity in mice. J Nutr 135: 2857–2861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

