Morphological Characterization of the Polyflux 210H Hemodialysis Filter Pores
- PMID: 23209902
- PMCID: PMC3502870
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/304135
Morphological Characterization of the Polyflux 210H Hemodialysis Filter Pores
Abstract
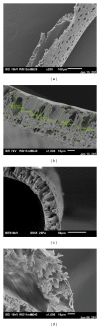
Background. Morphological characterization of hemodialysis membranes is necessary to improve pore design. Aim. To delineate membrane pore structure of a high flux filter, Polyflux 210H. Methods. We used a Joel JSM-6010LV scanning electron microscope (SEM) and a SU6600 Hitachi field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) to characterize the pore and fiber morphology. The maximal diameters of selected uremic toxins were calculated using the macromolecular modeling Crystallographic Object-Oriented Toolkit (COOT) software. Results. The mean pore densities on the outermost and innermost surfaces of the membrane were 36.81% and 5.45%, respectively. The membrane exhibited a tortuous structure with poor connection between the inner and outer pores. The aperture's width in the inner surface ranged between 34 and 45 nm, which is 8.76-11.60 times larger than the estimated maximum diameter of β2-microglobulin (3.88 nm). Conclusion. The results suggest that the diameter size of inner pore apertures is not a limiting factor to middle molecules clearance, the extremely diminished density is. Increasing inner pore density and improving channel structure are strategies to improve clearance of middle molecules.
Figures


References
-
- Sue B-H, Shi Y, Fu P, Tao Y, Nie S, Zhao C-S. Clinical evaluation of polyethersulfone high-flux hemodialysis membrane compared to other membranes. Journal of Applied Polymer Science . 2012;124:E91–E98.
-
- Rastogi A, Nissenson AR. Technological advances in renal replacement therapy: five years and beyond. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology . 2009;4(supplement 1):S132–S136. - PubMed
-
- Klinkmann H, Ivanovich P, Falkenhagen D. Biocompatibility: the need for a systems approach. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation . 1993;8(2):40–42. - PubMed
-
- Opatrný K. Clinical importance of biocompatibility and its effect on haemodialysis treatment. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation . 2003;18(supplement 5):V41–V44. - PubMed
-
- Subramanian S, Venkataraman R, Kellum JA. Influence of dialysis membranes on outcomes in acute renal failure: a meta-analysis. Kidney International . 2002;62(5):1819–1823. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

