Direct electrochemistry of Shewanella oneidensis cytochrome c nitrite reductase: evidence of interactions across the dimeric interface
- PMID: 23210513
- PMCID: PMC3566639
- DOI: 10.1021/bi3011708
Direct electrochemistry of Shewanella oneidensis cytochrome c nitrite reductase: evidence of interactions across the dimeric interface
Abstract
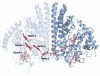
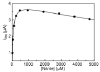
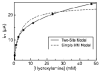
Shewanella oneidensis cytochrome c nitrite reductase (soNrfA), a dimeric enzyme that houses five c-type hemes per protomer, conducts the six-electron reduction of nitrite and the two-electron reduction of hydroxylamine. Protein film voltammetry (PFV) has been used to study the cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Escherichia coli (ecNrfA) previously, revealing catalytic reduction of both nitrite and hydroxylamine substrates by ecNrfA adsorbed to a graphite electrode that is characterized by "boosts" and attenuations in activity depending on the applied potential. Here, we use PFV to investigate the catalytic properties of soNrfA during both nitrite and hydroxylamine turnover and compare those properties to the properties of ecNrfA. Distinct differences in both the electrochemical and kinetic characteristics of soNrfA are observed; e.g., all detected electron transfer steps are one-electron in nature, contrary to what has been observed in ecNrfA [Angove, H. C., Cole, J. A., Richardson, D. J., and Butt, J. N. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23374-23381]. Additionally, we find evidence of substrate inhibition during nitrite turnover and negative cooperativity during hydroxylamine turnover, neither of which has previously been observed in any cytochrome c nitrite reductase. Collectively, these data provide evidence that during catalysis, potential pathways of communication exist between the individual soNrfA monomers comprising the native homodimer.
Figures



References
-
- Simon J. Enzymology and bioenergetics of respiratory nitrite ammonification. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002;26:285–309. - PubMed
-
- Pope NR, Cole JA. Generation of a membrane potential by one of two independent pathways for nitrite reduction by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1982;128:219–222. - PubMed
-
- Gao H, Yang ZK, Barua S, Reed SB, Romine MF, Nealson KH, Fredrickson JK, Tiedje JM, Zhou J. Reduction of nitrate in Shewanella oneidensis depends on atypical NAP and NRF systems with NapB as a preferred electron transport protein from CymA to NapA. ISME J. 2009;3:966–976. - PubMed
-
- Stach P, Einsle O, Schumacher W, Kurun E, Kroneck PM. Bacterial cytochrome c nitrite reductase: new structural and functional aspects. J Inorg Biochem. 2000;79:381–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

