Xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptors involved in drug metabolism: a structural perspective
- PMID: 23210723
- PMCID: PMC4878694
- DOI: 10.3109/03602532.2012.740049
Xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptors involved in drug metabolism: a structural perspective
Abstract
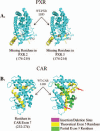
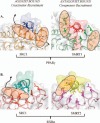
Xenobiotic compounds undergo a critical range of biotransformations performed by the phase I, II, and III drug-metabolizing enzymes. The oxidation, conjugation, and transportation of potentially harmful xenobiotic and endobiotic compounds achieved by these catalytic systems are significantly regulated, at the gene expression level, by members of the nuclear receptor (NR) family of ligand-modulated transcription factors. Activation of NRs by a variety of endo- and exogenous chemicals are elemental to induction and repression of drug-metabolism pathways. The master xenobiotic sensing NRs, the promiscuous pregnane X receptor and less-promiscuous constitutive androstane receptor are crucial to initial ligand recognition, jump-starting the metabolic process. Other receptors, including farnesoid X receptor, vitamin D receptor, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor, glucocorticoid receptor, liver X receptor, and RAR-related orphan receptor, are not directly linked to promiscuous xenobiotic binding, but clearly play important roles in the modulation of metabolic gene expression. Crystallographic studies of the ligand-binding domains of nine NRs involved in drug metabolism provide key insights into ligand-based and constitutive activity, coregulator recruitment, and gene regulation. Structures of other, noncanonical transcription factors also shed light on secondary, but important, pathways of control. Pharmacological targeting of some of these nuclear and atypical receptors has been instituted as a means to treat metabolic and developmental disorders and provides a future avenue to be explored for other members of the xenobiotic-sensing NRs.
Figures





References
-
- Aleksunes LM, Manautou JE. Emerging role of Nrf2 in protecting against hepatic and gastrointestinal disease. Toxicol Pathol. 2007;35:459–473. - PubMed
-
- Alnouti Y, Klaassen CD. Regulation of sulfotransferase enzymes by prototypical microsomal enzyme inducers in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324:612–621. - PubMed
-
- André E, Gawlas K, Becker-André M. A novel isoform of the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta is specifically expressed in pineal gland and retina. Gene. 1998;216:277–283. - PubMed
-
- Arita K, Nanda A, Wessagowit V, Akiyama M, Alsaleh QA, McGrath JA. A novel mutation in the VDR gene in hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:168–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
