Digitoxin and its analogs as novel cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 23210930
- PMCID: PMC3506989
- DOI: 10.1186/2162-3619-1-4
Digitoxin and its analogs as novel cancer therapeutics
Abstract
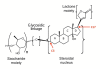
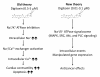
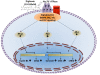
A growing body of evidence indicates that digitoxin cardiac glycoside is a promising anticancer agent when used at therapeutic concentrations. Digitoxin has a prolonged half-life and a well-established clinical profile. New scientific avenues have shown that manipulating the chemical structure of the saccharide moiety of digitoxin leads to synthetic analogs with increased cytotoxic activity. However, the anticancer mechanism of digitoxin or synthetic analogs is still subject to study while concerns about digitoxin's cardiotoxicity preclude its clinical application in cancer therapeutics. This review focuses on digitoxin and its analogs, and their cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Moreover, a new perspective on the pharmacological aspects of digitoxin and its analogs is provided to emphasize new research directions for developing potent chemotherapeutic drugs.
Figures

References
-
- Huxtable RJ. The Erroneous Pharmacology of a Cat. Mol Interv. 2001;1(2):75–77. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

