Regulation of the human hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase (SULT2A1) by RORα and RORγ and its potential relevance to human liver diseases
- PMID: 23211525
- PMCID: PMC3545217
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2012-1145
Regulation of the human hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase (SULT2A1) by RORα and RORγ and its potential relevance to human liver diseases
Abstract
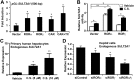
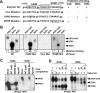
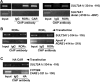
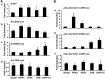
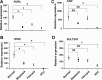
The retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs) were postulated to have functions in tissue development and circadian rhythm. In this study, we revealed a novel function of RORα (NR1F1) and RORγ (NR1F3) in regulating the human hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase (SULT2A1), a phase II conjugating enzyme known to sulfonate bile acids, hydroxysteroid dehydroepiandrosterone, and related androgens. A combination of promoter reporter gene assay and EMSA and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays showed that both RORα and RORγ transactivated the SULT2A1 gene promoter through their binding to a ROR response element found in the SULT2A1 gene promoter. Interestingly, this ROR response element overlaps with a previously reported constitutive androstane receptor response element on the same promoter. Down-regulation of RORα and/or RORγ by small interfering RNA inhibited the expression of endogenous SULT2A1. In primary human hepatocytes and human livers, we found a positive correlation between the expression of SULT2A1 and RORs, which further supported the regulation of SULT2A1 by RORs. We also found that the expression of RORα and RORγ was impaired in several liver disease conditions, such as steatosis/steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The positive regulation of human SULT2A1 by RORs is opposite to the negative regulation of Sult2a1 by RORs in rodents. In summary, our results established SULT2A1 as a novel ROR target gene. The expression of RORs is a potential predictor for the expression of SULT2A1 as well as disease conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Jetten AM, Kurebayashi S, Ueda E. 2001. The ROR nuclear orphan receptor subfamily: critical regulators of multiple biological processes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 69:205–247 - PubMed
-
- Carlberg C, Hooft van Huijsduijnen R, Staple JK, DeLamarter JF, Becker-André M. 1994. RZRs, a new family of retinoid-related orphan receptors that function as both monomers and homodimers. Mol Endocrinol 8:757–770 - PubMed
-
- Hamilton BA, Frankel WN, Kerrebrock AW, Hawkins TL, FitzHugh W, Kusumi K, Russell LB, Mueller KL, van Berkel V, Birren BW, Kruglyak L, Lander ES. 1996. Disruption of the nuclear hormone receptor RORα in staggerer mice. Nature 379:736–739 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

