Epitope interactions of monoclonal antibodies targeting CD20 and their relationship to functional properties
- PMID: 23211638
- PMCID: PMC3564883
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.22771
Epitope interactions of monoclonal antibodies targeting CD20 and their relationship to functional properties
Abstract
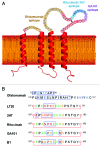
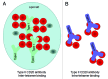
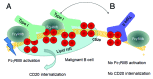
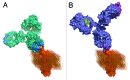
Several novel anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies are currently in development with the aim of improving the treatment of B cell malignancies. Mutagenesis and epitope mapping studies have revealed differences between the CD20 epitopes recognized by these antibodies. Recently, X-ray crystallography studies confirmed that the Type I CD20 antibody rituximab and the Type II CD20 antibody obinutuzumab (GA101) differ fundamentally in their interaction with CD20 despite recognizing a partially overlapping epitope on CD20. The Type I CD20 antibodies rituximab and ofatumumab are known to bind to different epitopes. The differences suggest that the biological properties of these antibodies are not solely determined by their core epitope sequences, but also depend on other factors, such as the elbow hinge angle, the orientation of the bound antibody and differential effects mediated by the Fc region of the antibody. Taken together, these factors may explain differences in the preclinical properties and clinical efficacy of anti-CD20 antibodies.
Figures


Comment in
-
Response to: monoclonal antibodies targeting CD20.MAbs. 2013 May-Jun;5(3):337-8. doi: 10.4161/mabs.24108. Epub 2013 Mar 14. MAbs. 2013. PMID: 23493087 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD20.MAbs. 2013 May-Jun;5(3):335-6. doi: 10.4161/mabs.24106. Epub 2013 Mar 14. MAbs. 2013. PMID: 23493149 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stashenko P, Nadler LM, Hardy R, Schlossman SF. Characterization of a human B lymphocyte-specific antigen. J Immunol. 1980;125:1678–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
