Initiation of DNA damage responses through XPG-related nucleases
- PMID: 23211746
- PMCID: PMC3553381
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.322
Initiation of DNA damage responses through XPG-related nucleases
Abstract
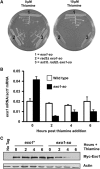
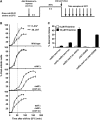
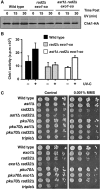
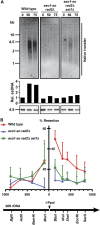
Lesion-specific enzymes repair different forms of DNA damage, yet all lesions elicit the same checkpoint response. The common intermediate required to mount a checkpoint response is thought to be single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), coated by replication protein A (RPA) and containing a primer-template junction. To identify factors important for initiating the checkpoint response, we screened for genes that, when overexpressed, could amplify a checkpoint signal to a weak allele of chk1 in fission yeast. We identified Ast1, a novel member of the XPG-related family of endo/exonucleases. Ast1 promotes checkpoint activation caused by the absence of the other XPG-related nucleases, Exo1 and Rad2, the homologue of Fen1. Each nuclease is recruited to DSBs, and promotes the formation of ssDNA for checkpoint activation and recombinational repair. For Rad2 and Exo1, this is independent of their S-phase role in Okazaki fragment processing. This XPG-related pathway is distinct from MRN-dependent responses, and each enzyme is critical for damage resistance in MRN mutants. Thus, multiple nucleases collaborate to initiate DNA damage responses, highlighting the importance of these responses to cellular fitness.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

