Occurrence of Ochratoxin A in the wild boar (Sus scrofa): chemical and histological analysis
- PMID: 23211797
- PMCID: PMC3528255
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins4121440
Occurrence of Ochratoxin A in the wild boar (Sus scrofa): chemical and histological analysis
Abstract
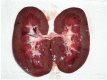
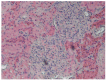
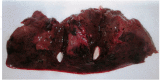
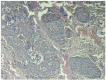
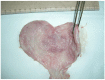
Ochratoxins are fungal secondary metabolites that may contaminate a broad variety of foodstuffs, such as grains, vegetables, coffee, dried fruits, beer, wine and meats. Ochratoxins are nephrotoxins, carcinogens, teratogens and immunotoxins in rats and are also likely to be in humans. In 2009/2010, a survey of the presence of Ochratoxin A (OTA) in regularly hunted wild boars in the Calabria region of southern Italy detected OTA in 23 animals in the kidney, urinary bladder, liver and muscles: 1.1 ± 1.15, 0.6 ± 0.58, 0.5 ± 0.54 and 0.3 ± 0.26 μg/kg, respectively. Twelve tissue samples showed levels of OTA higher than the guideline level (1 μg/kg) established by the Italian Ministry of Health. In five wild boars, gross-microscopic lesions were described for the organs displaying the highest concentrations of OTA determined by HPLC-FLD analysis, i.e., the kidney, liver and urinary bladder.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Determination of ochratoxin A in tissues of wild boar (Sus scrofa L.) by enzymatic digestion (ED) coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with a fluorescence detector (HPLC-FLD).Mycotoxin Res. 2018 Mar;34(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s12550-017-0292-z. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Mycotoxin Res. 2018. PMID: 28856595
-
Ochratoxin A Levels in Tissues of Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Northern Italy.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 8;12(11):706. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110706. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33171643 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Ochratoxin A in Tissues of Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Southern Italy.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;17(2):74. doi: 10.3390/toxins17020074. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39998091 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of ochratoxin A in commodities and processed food--a review of EU occurrence data.Food Addit Contam. 2005;22 Suppl 1:26-30. doi: 10.1080/02652030500344811. Food Addit Contam. 2005. PMID: 16332618 Review.
-
The Occurrence and Contamination Level of Ochratoxin A in Plant and Animal-Derived Food Commodities.Molecules. 2021 Nov 17;26(22):6928. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226928. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34834020 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Initial Detection of Mycotoxins Released and Accumulated in the Golden Jackal (Canis aureus): Investigating the Potential of Carnivores as Environmental Bioindicators.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 16;26(8):3755. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083755. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332407 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of ochratoxin A in tissues of wild boar (Sus scrofa L.) by enzymatic digestion (ED) coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with a fluorescence detector (HPLC-FLD).Mycotoxin Res. 2018 Mar;34(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s12550-017-0292-z. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Mycotoxin Res. 2018. PMID: 28856595
-
Occurrence of ochratoxin A in typical salami produced in different regions of Italy.Mycotoxin Res. 2019 May;35(2):141-148. doi: 10.1007/s12550-018-0338-x. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Mycotoxin Res. 2019. PMID: 30460520
-
Assessment of Ochratoxin A Exposure in Ornamental and Self-Consumption Backyard Chickens.Vet Sci. 2020 Feb 7;7(1):18. doi: 10.3390/vetsci7010018. Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32046067 Free PMC article.
-
Ochratoxin A Levels in Tissues of Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Northern Italy.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 8;12(11):706. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110706. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33171643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peterson S.W. Phylogenetic Relationships in Aspergillus Based on rDNA Sequence Analysis. In: Samson R.A., Pitt J.R., editors. Classification of Penicillium and Aspergillus: Integration of Modern Taxonomic Methods. Harwood Academic Publishers; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2000. pp. 323–356.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

