MicroRNA-205 directly regulates the tumor suppressor, interleukin-24, in human KB oral cancer cells
- PMID: 23212344
- PMCID: PMC3887855
- DOI: 10.1007/s10059-013-2154-7
MicroRNA-205 directly regulates the tumor suppressor, interleukin-24, in human KB oral cancer cells
Abstract
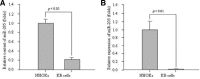
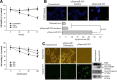
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a form of small noncoding RNA that regulates the expression of genes either by inhibiting mRNA translation or by inducing its degradation. Small microRNA play important roles in regulating a large number of cellular processes, including development, proliferation and apoptosis. This study examined the biological functions of miR-205 as a tumor suppressor in KB oral cancer cells. The results showed that miR-205 expression was significantly lower in KB oral cancer cells than in human normal oral keratinocytes. Furthermore, the miR-205 over-expressed in KB oral cancer cells increased the cell cytotoxicity and induced apoptosis through the activation of caspase-3/-7. The transfection of miR-205 into KB oral cancer cells strongly induced IL-24, a well known cytokine that acts as a tumor suppressor in a range of tumor tissues. In addition, miR-205 targeted the IL-24 promoter directly to induce gene expression. Overall, miR-205 has significant therapeutic potential to turn on silenced tumor suppressor genes by targeting them with miRNA.
Figures




References
-
- Adachi R., Horiuchi S., Sakurazawa Y., Hasegawa T., Sato K., Sakamaki T. ErbB2 down-regulates microRNA-205 in breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011;411:804–808. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich I. A postulated role for microRNA in cellular differentiation. FASEB J. 2005;19:875–879. - PubMed
-
- Boll K., Reiche K., Kasack K., Morbt N., Kretzschmar A.K., Tomm J.M., Verhaegh G., Schalken J., von Bergen M., Horn F., et al. MiR-130a, miR-203 and miR-205 jointly repress key oncogenic pathways and are downregulated in prostate carcinoma. Oncogene. 2012 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Bonnet E., Wuyts J., Rouze P., Van de Peer Y. Evidence that microRNA precursors, unlike other non-coding RNAs, have lower folding free energies than random sequences. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:2911–2917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

