Effect of timing of dialysis commencement on clinical outcomes of patients with planned initiation of peritoneal dialysis in the IDEAL trial
- PMID: 23212859
- PMCID: PMC3524893
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2012.00046
Effect of timing of dialysis commencement on clinical outcomes of patients with planned initiation of peritoneal dialysis in the IDEAL trial
Abstract
Background: Since the mid-1990s, early dialysis initiation has dramatically increased in many countries. The Initiating Dialysis Early and Late (IDEAL) study demonstrated that, compared with late initiation, planned early initiation of dialysis was associated with comparable clinical outcomes and increased health care costs. Because residual renal function is a key determinant of outcome and is better preserved with peritoneal dialysis (PD), the present pre-specified subgroup analysis of the IDEAL trial examined the effects of early-compared with late-start dialysis on clinical outcomes in patients whose planned therapy at the time of randomization was PD.
Methods: Adults with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 10 - 15 mL/min/1.73 m(2) who planned to be treated with PD were randomly allocated to commence dialysis at an eGFR of 10 - 14 mL/min/1.73 m(2) (early start) or 5 - 7 mL/min/1.73 m(2) (late start). The primary outcome was all-cause mortality.
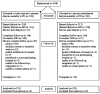
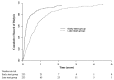
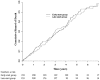
Results: Of the 828 IDEAL trial participants, 466 (56%) planned to commence PD and were randomized to early start (n = 233) or late start (n = 233). The median times from randomization to dialysis initiation were, respectively, 2.03 months [interquartile range (IQR):1.67 - 2.30 months] and 7.83 months (IQR: 5.83 - 8.83 months). Death occurred in 102 early-start patients and 96 late-start patients [hazard ratio: 1.04; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.79 - 1.37]. No differences in composite cardiovascular events, composite infectious deaths, or dialysis-associated complications were observed between the groups. Peritonitis rates were 0.73 episodes (95% CI: 0.65 - 0.82 episodes) per patient-year in the early-start group and 0.69 episodes (95% CI: 0.61 - 0.78 episodes) per patient-year in the late-start group (incidence rate ratio: 1.19; 95% CI: 0.86 - 1.65; p = 0.29). The proportion of patients planning to commence PD who actually initiated dialysis with PD was higher in the early-start group (80% vs 70%, p = 0.01).
Conclusion: Early initiation of dialysis in patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease who planned to be treated with PD was associated with clinical outcomes comparable to those seen with late dialysis initiation. Compared with early-start patients, late-start patients who had chosen PD as their planned dialysis modality were less likely to commence on PD.
Figures
References
-
- Rosansky S, Glassock RJ, Clark WF. Early start of dialysis: a critical review. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2011; 6:1222–8 - PubMed
-
- Cooper BA, Branley P, Bulfone L, Collins JF, Craig JC, Fraenkel MB, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of early versus late initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med 2010; 363:609–19 - PubMed
-
- Harris A, Cooper BA, Li JJ, Bulfone L, Branley P, Collins JF, et al. Cost-effectiveness of initiating dialysis early: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis 2011; 57:707–15 - PubMed
-
- Lysaght MJ, Vonesh EF, Gotch F, Ibels L, Keen M, Lindholm B, et al. The influence of dialysis treatment modality on the decline of remaining renal function. ASAIO Trans 1991; 37:598–604 - PubMed
-
- Canacarini G, Bunori G, Camerini C, Brasa S, Manili L, Maiorca R. Renal function recovery and maintenance of residual diuresis in CAPD and hemodialysis. Perit Dial Bull 1986; 6:77–9
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

