Toll-like receptor agonists and febrile range hyperthermia synergize to induce heat shock protein 70 expression and extracellular release
- PMID: 23212905
- PMCID: PMC3554941
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.427336
Toll-like receptor agonists and febrile range hyperthermia synergize to induce heat shock protein 70 expression and extracellular release
Abstract
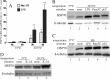
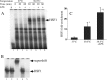
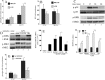
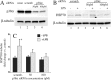
Heat shock protein (Hsp) 70 expression can be stimulated by febrile range temperature (FRT). Hsp70 has been shown to be elevated in serum of patients with sepsis, and when released from cells, extracellular Hsp70 exerts endotoxin-like effects through Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) receptors. Circulating TLR agonists and fever both persist for the first several days of sepsis, and each can activate Hsp70 expression; however, the effect of combined exposure to FRT and TLR agonists on Hsp70 expression is unknown. We found that concurrent exposure to FRT (39.5 °C) and agonists for TLR4 (LPS), TLR2 (Pam3Cys), or TLR3 (poly(IC)) synergized to increase Hsp70 expression and extracellular release in RAW264.7 macrophages. The increase in Hsp70 expression was associated with activation of p38 and ERK MAP kinases, phosphorylation of histone H3, and increased recruitment of HSF1 to the Hsp70 promoter. Pretreatment with the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB283580 but not the ERK pathway inhibitor UO126 significantly reduced Hsp70 gene modification and Hsp70 expression in RAW cells co-exposed to LPS and FRT. In mice challenged with intratracheal LPS and then exposed to febrile range hyperthermia (core temperature, ∼39.5 °C), Hsp70 levels in lung tissue and in cell-free lung lavage were increased compared with mice exposed to either hyperthermia or LPS alone. We propose a model of how enhanced Hsp70 expression and extracellular release in patients concurrently exposed to fever and TLR agonists may contribute to the pathogenesis of sepsis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide augments febrile-range hyperthermia-induced heat shock protein 70 expression and extracellular release in human THP1 cells.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0118010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118010. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25659128 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock up-regulates expression of Toll-like receptor-2 and Toll-like receptor-4 in human monocytes via p38 kinase signal pathway.Immunology. 2005 Apr;114(4):522-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.02112.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 15804289 Free PMC article.
-
Febrile-range temperature modifies cytokine gene expression in LPS-stimulated macrophages by differentially modifying NF-{kappa}B recruitment to cytokine gene promoters.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Jan;298(1):C171-81. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00346.2009. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19846753 Free PMC article.
-
Fever, hyperthermia and the heat shock response.Int J Hyperthermia. 2013 Aug;29(5):423-35. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2013.808766. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Int J Hyperthermia. 2013. PMID: 23863046 Review.
-
LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes.Cell Signal. 2001 Feb;13(2):85-94. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(00)00149-2. Cell Signal. 2001. PMID: 11257452 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-Induced Hyperthermia Review.Cureus. 2022 Jul 26;14(7):e27278. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27278. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36039261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide augments febrile-range hyperthermia-induced heat shock protein 70 expression and extracellular release in human THP1 cells.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0118010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118010. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25659128 Free PMC article.
-
Monophosphoryl lipid A as a co-adjuvant in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus vaccine development: improvement of immune responses in a mouse model of infection.Immunol Res. 2024 Jun;72(3):490-502. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09456-x. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38383811
-
A role for heat shock factor 1 in hypercapnia-induced inhibition of inflammatory cytokine expression.FASEB J. 2018 Jul;32(7):3614-3622. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701164R. Epub 2018 Feb 5. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29405096 Free PMC article.
-
Role of heat shock protein 70 in regulation of anti-inflammatory response to curcumin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Nutr Res Pract. 2023 Jun;17(3):397-407. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.3.397. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Nutr Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37266116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sriskandan S., Altmann D. M. (2008) The immunology of sepsis. J. Pathol. 214, 211–223 - PubMed
-
- Bianchi M. E. (2007) DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins. All we need to know about danger. J. Leukocyte Biol. 81, 1–5 - PubMed
-
- Shi Y., Evans J. E., Rock K. L. (2003) Molecular identification of a danger signal that alerts the immune system to dying cells. Nature 425, 516–521 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

