Regulation of the G-protein regulatory-Gαi signaling complex by nonreceptor guanine nucleotide exchange factors
- PMID: 23212907
- PMCID: PMC3561525
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418467
Regulation of the G-protein regulatory-Gαi signaling complex by nonreceptor guanine nucleotide exchange factors
Abstract
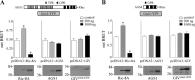
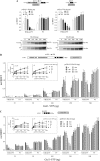
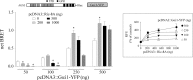
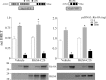
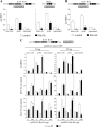
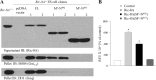
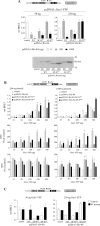
Group II activators of G-protein signaling (AGS) serve as binding partners for Gα(i/o/t) via one or more G-protein regulatory (GPR) motifs. GPR-Gα signaling modules may be differentially regulated by cell surface receptors or by different nonreceptor guanine nucleotide exchange factors. We determined the effect of the nonreceptor guanine nucleotide exchange factors AGS1, GIV/Girdin, and Ric-8A on the interaction of two distinct GPR proteins, AGS3 and AGS4, with Gα(il) in the intact cell by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. AGS3-Rluc-Gα(i1)-YFP and AGS4-Rluc-Gα(i1)-YFP BRET were regulated by Ric-8A but not by Gα-interacting vesicle-associated protein (GIV) or AGS1. The Ric-8A regulation was biphasic and dependent upon the amount of Ric-8A and Gα(i1)-YFP. The inhibitory regulation of GPR-Gα(i1) BRET by Ric-8A was blocked by pertussis toxin. The enhancement of GPR-Gα(i1) BRET observed with Ric-8A was further augmented by pertussis toxin treatment. The regulation of GPR-Gα(i) interaction by Ric-8A was not altered by RGS4. AGS3-Rluc-Gα(i1)-YFP and AGS4-Rluc-G-Gα(i1)-YFP BRET were observed in both pellet and supernatant subcellular fractions and were regulated by Ric-8A in both fractions. The regulation of the GPR-Gα(i1) complex by Ric-8A, as well as the ability of Ric-8A to restore Gα expression in Ric8A(-/-) mouse embryonic stem cells, involved two helical domains at the carboxyl terminus of Ric-8A. These data indicate a dynamic interaction between GPR proteins, Gα(i1) and Ric-8A, in the cell that influences subcellular localization of the three proteins and regulates complex formation.
Figures
References
-
- Cismowski M. J., Takesono A., Ma C., Lizano J. S., Xie X., Fuernkranz H., Lanier S. M., Duzic E. (1999) Genetic screens in yeast to identify mammalian nonreceptor modulators of G-protein signaling. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 878–883 - PubMed
-
- Takesono A., Cismowski M. J., Ribas C., Bernard M., Chung P., Hazard S., 3rd, Duzic E., Lanier S. M. (1999) Receptor-independent activators of heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33202–33205 - PubMed
-
- Du Q., Stukenberg P. T., Macara I. G. (2001) A mammalian Partner of inscuteable binds NuMA and regulates mitotic spindle organization. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 1069–1075 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

