Cancer therapy-induced cardiac toxicity in early breast cancer: addressing the unresolved issues
- PMID: 23212997
- PMCID: PMC3667651
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.100560
Cancer therapy-induced cardiac toxicity in early breast cancer: addressing the unresolved issues
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

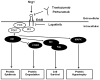
References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Cho H, Mariotto A, Eisner MP, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA, editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations) National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: Apr, 2012. [Accessed June 29, 2012]. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09/, based on November 2011 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site.
-
- Hooning MJ, Botma A, Aleman BM, Baaijens MH, Bartelink H, Klijn JG, Taylor CW, van Leeuwen FE. Long-term risk of cardiovascular disease in 10-year survivors of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:365–375. - PubMed
-
- Von Hoff DD, Layard MW, Basa P, Davis HL, Jr, Von Hoff AL, Rozencweig M, Muggia FM. Risk factors for doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann Intern Med. 1979;91:710–717. - PubMed
-
- Swain SM, Whaley FS, Ewer MS. Congestive heart failure in patients treated with doxorubicin: A retrospective analysis of three trials. Cancer. 2003;97:2869–2879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

