SLC1A5 mediates glutamine transport required for lung cancer cell growth and survival
- PMID: 23213057
- PMCID: PMC3697078
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2334
SLC1A5 mediates glutamine transport required for lung cancer cell growth and survival
Abstract
Purpose: We have previously identified solute-linked carrier family A1 member 5 (SLC1A5) as an overexpressed protein in a shotgun proteomic analysis of stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) when compared with matched controls. We hypothesized that overexpression of SLC1A5 occurs to meet the metabolic demand for lung cancer cell growth and survival.
Experimental design: To test our hypothesis, we first analyzed the protein expression of SLC1A5 in archival lung cancer tissues by immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting (N = 98) and in cell lines (N = 36). To examine SLC1A5 involvement in amino acid transportation, we conducted kinetic analysis of l-glutamine (Gln) uptake in lung cancer cell lines in the presence and absence of a pharmacologic inhibitor of SLC1A5, gamma-l-Glutamyl-p-Nitroanilide (GPNA). Finally, we examined the effect of Gln deprivation and uptake inhibition on cell growth, cell-cycle progression, and growth signaling pathways of five lung cancer cell lines.
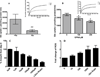
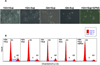
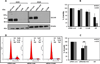
Results: Our results show that (i) SLC1A5 protein is expressed in 95% of squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), 74% of adenocarcinomas (ADC), and 50% of neuroendocrine tumors; (ii) SLC1A5 is located at the cytoplasmic membrane and is significantly associated with SCC histology and male gender; (iii) 68% of Gln is transported in a Na(+)-dependent manner, 50% of which is attributed to SLC1A5 activity; and (iv) pharmacologic and genetic targeting of SLC1A5 decreased cell growth and viability in lung cancer cells, an effect mediated in part by mTOR signaling.
Conclusions: These results suggest that SLC1A5 plays a key role in Gln transport controlling lung cancer cells' metabolism, growth, and survival.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman PC, Mauer AM, Vokes EE. Lung cancer. Lancet. 2000;355:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Carbone DP. Molecular modalities in the treatment of lung cancer. Oncology (Huntingt) 1999;13:142–147. - PubMed
-
- Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–1203. - PubMed
-
- Campa MJ, Wang MZ, Howard B, Fitzgerald MC, Patz EF., Jr Protein expression profiling identifies macrophage migration inhibitory factor and cyclophilin a as potential molecular targets in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1652–1656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

