Positron emission tomography/computed tomography identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from the REDECT trial
- PMID: 23213092
- PMCID: PMC5795663
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.2445
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from the REDECT trial
Erratum in
-
Errata.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jan 1;36(1):98. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.9950. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29281805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: A clinical study to characterize renal masses with positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) was undertaken.
Patients and methods: This was an open-label multicenter study of iodine-124 ((124)I) -girentuximab PET/CT in patients with renal masses who were scheduled for resection. PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) of the abdomen were performed 2 to 6 days after intravenous (124)I-girentuximab administration and before resection of the renal mass(es). Images were interpreted centrally by three blinded readers for each imaging modality. Tumor histology was determined by a blinded central pathologist. The primary end points-average sensitivity and specificity for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC)-were compared between the two modalities. Agreement between and within readers was assessed.
Results: (124)I-girentuximab was well tolerated. In all, 195 patients had complete data sets (histopathologic diagnosis and PET/CT and CECT results) available. The average sensitivity was 86.2% (95% CI, 75.3% to 97.1%) for PET/CT and 75.5% (95% CI, 62.6% to 88.4%) for CECT (P = .023). The average specificity was 85.9% (95% CI, 69.4% to 99.9%) for PET/CT and 46.8% (95% CI, 18.8% to 74.7%) for CECT (P = .005). Inter-reader agreement was high (κ range, 0.87 to 0.92 for PET/CT; 0.67 to 0.76 for CECT), as was intrareader agreement (range, 87% to 100% for PET/CT; 73.7% to 91.3% for CECT).
Conclusion: This study represents (to the best of our knowledge) the first clinical validation of a molecular imaging biomarker for malignancy. (124)I-girentuximab PET/CT can accurately and noninvasively identify ccRCC, with potential utility for designing best management approaches for patients with renal masses.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00606632.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
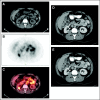
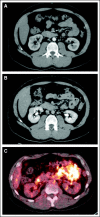
Comment in
-
Imaging: Red light warning sign for clear-cell renal cell carcinoma--REDECT reveals imaging biomarker.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013 Feb;10(2):63. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2012.232. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23247374 No abstract available.
-
Kidney cancer: PET-CT successfully identifies ccRCC.Nat Rev Urol. 2013 Feb;10(2):64. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2012.248. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Nat Rev Urol. 2013. PMID: 23247692 No abstract available.
-
Re: positron emission tomography/computed tomography identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from the REDECT trial.J Urol. 2013 Aug;190(2):493. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.04.067. Epub 2013 Apr 27. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23845328 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel R Ward E Brawley O , etal: Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths CA Cancer J Clin 61: 212– 236,2011 - PubMed
-
- Linehan WM, Walther MM, Zbar B: The genetic basis of cancer of the kidney J Urol 170: 2163– 2172,2003 - PubMed
-
- Gill IS Aron M Gervais DA , etal: Small renal mass N Engl J Med 362: 624– 634,2010 - PubMed
-
- Kattan MW Reuter V Motzer RJ , etal: A postoperative prognostic nomogram for renal cell carcinoma J Urol 166: 63– 67,2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

