Isolation of novel prototype galectins from the marine ball sponge Cinachyrella sp. guided by their modulatory activity on mammalian glutamate-gated ion channels
- PMID: 23213112
- PMCID: PMC3581077
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cws165
Isolation of novel prototype galectins from the marine ball sponge Cinachyrella sp. guided by their modulatory activity on mammalian glutamate-gated ion channels
Abstract
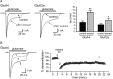
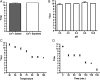
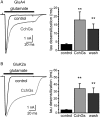
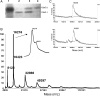
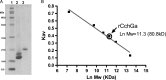
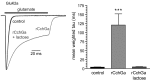
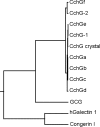
Here we report the bioactivity-guided isolation of novel galectins from the marine sponge Cinachyrella sp., collected from Iriomote Island, Japan. The lectin proteins, which we refer to as the Cinachyrella galectins (CchGs), were identified as the active principles in an aqueous sponge extract that modulated the function of mammalian ionotropic glutamate receptors. Aggregation of rabbit erythrocytes by CchGs was competed most effectively by galactosides but not mannose, a profile characteristic of members of the galectin family of oligosaccharide-binding proteins. The lectin activity was remarkably stable, with only a modest loss in hemagglutination after exposure of the protein to 100°C for 1 h, and showed little sensitivity to calcium concentration. CchG-1 and -2 appeared as 16 and 18 kDa in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, respectively, whereas matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry indicated broad ion clusters centered at 16,216 and 16,423, respectively. The amino acid sequences of the CchGs were deduced using a combination of Edman degradation and cDNA cloning and revealed that the proteins were distant orthologs of animal prototype galectins and that multiple isolectins comprised the CchGs. One of the isolectins was expressed as a recombinant protein and exhibited physico-chemical and biological properties comparable with those of the natural lectins. The biochemical properties of the CchGs as well as their unexpected activity on mammalian excitatory amino acid receptors suggest that further analysis of these new members of the galectin family will yield further glycobiological and neurophysiological insights.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of a tetrameric galectin from Cinachyrella sp. (ball sponge).Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012 Sep;68(Pt 9):1163-74. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912022834. Epub 2012 Aug 18. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012. PMID: 22948917 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, purification, characterization and glycan-binding profile of a d-galactoside specific lectin from the marine sponge, Halichondria okadai.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 Aug;150(4):349-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2008.04.004. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18534886
-
Halilectin 1 (H-1) and Halilectin 2 (H-2): two new lectins isolated from the marine sponge Haliclona caerulea.J Mol Recognit. 2013 Jan;26(1):51-8. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2243. J Mol Recognit. 2013. PMID: 23280618
-
Oligosaccharide specificity of galectins: a search by frontal affinity chromatography.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Sep 19;1572(2-3):232-54. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00311-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12223272 Review.
-
Regulatory roles of galectins in the immune response.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005 Apr;136(4):385-400. doi: 10.1159/000084545. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15775687 Review.
Cited by
-
Porifera Lectins: Diversity, Physiological Roles and Biotechnological Potential.Mar Drugs. 2015 Aug 7;13(8):5059-101. doi: 10.3390/md13085059. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26262628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of ionotropic glutamate receptor function by vertebrate galectins.J Physiol. 2014 May 15;592(10):2079-96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.269597. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24614744 Free PMC article.
-
Marine sponge lectins: actual status on properties and biological activities.Molecules. 2014 Dec 26;20(1):348-57. doi: 10.3390/molecules20010348. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25549059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of HOL-30: a novel tandem-repeat galectin from the marine sponge Halichondria okadai.BBA Adv. 2025 Mar 15;7:100153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2025.100153. eCollection 2025. BBA Adv. 2025. PMID: 40207211 Free PMC article.
-
Afil, a Lectin from Aplysina fistularis, Exhibits Antibiofilm and Synergistic Antibacterial Activity Against Resistant Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 10;13(6):1349. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061349. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atta AM, Barral-Netto M, Peixinho S, Sousa-Atta ML. Isolation and functional characterization of a mitogenic lectin from the marine sponge Cinachyrella alloclada. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1989;22:379–385. - PubMed
-
- Brakenhoff RH, Schoenmakers JG, Lubsen NH. Chimeric cDNA clones: A novel PCR artifact. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19:1949. doi:10.1093/nar/19.8.1949. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Camby I, Belot N, Rorive S, Lefranc F, Maurage CA, Lahm H, Kaltner H, Hadari Y, Ruchoux MM, Brotchi J, et al. Galectins are differentially expressed in supratentorial pilocytic astrocytomas, astrocytomas, anaplastic astrocytomas and glioblastomas, and significantly modulate tumor astrocyte migration. Brain Pathol. 2001;11:12–26. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2001.tb00377.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Lella S, Sundblad V, Cerliani JP, Guardia CM, Estrin DA, Vasta GR, Rabinovich GA. When galectins recognize glycans: From biochemistry to physiology and back again. Biochemistry. 2011;50:7842–7857. doi:10.1021/bi201121m. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

