In urban and rural India, a standardized patient study showed low levels of provider training and huge quality gaps
- PMID: 23213162
- PMCID: PMC3730274
- DOI: 10.1377/hlthaff.2011.1356
In urban and rural India, a standardized patient study showed low levels of provider training and huge quality gaps
Abstract
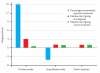
This article reports on the quality of care delivered by private and public providers of primary health care services in rural and urban India. To measure quality, the study used standardized patients recruited from the local community and trained to present consistent cases of illness to providers. We found low overall levels of medical training among health care providers; in rural Madhya Pradesh, for example, 67 percent of health care providers who were sampled reported no medical qualifications at all. What's more, we found only small differences between trained and untrained doctors in such areas as adherence to clinical checklists. Correct diagnoses were rare, incorrect treatments were widely prescribed, and adherence to clinical checklists was higher in private than in public clinics. Our results suggest an urgent need to measure the quality of health care services systematically and to improve the quality of medical education and continuing education programs, among other policy changes.
Figures


Comment in
-
A standardised patient study of primary healthcare services.Indian J Med Ethics. 2013 Apr-Jun;10(2):128-9. doi: 10.20529/IJME.2013.039. Indian J Med Ethics. 2013. PMID: 23697497 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rao M, Rao KD, Kumar AK, Chatterjee M, Sundararaman T. Human resources for health in India. Lancet. 2011;377(9765):587–98. - PubMed
-
- Das J, Gertler PJ. Variations in practice quality in five low-income countries: a conceptual overview. Health Aff (Millwood) 2007;26(3):w296–309. DOI: 10.1377/hlthaff.26.3.w296. - PubMed
-
- Leonard KL, Masatu MC, Vialou A. Getting doctors to do their best: the roles of ability and motivation in health care quality. J Hum Resour. 2007;42(3):682–700.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

