Motor transport of self-assembled cargos in crowded environments
- PMID: 23213204
- PMCID: PMC3529018
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1209304109
Motor transport of self-assembled cargos in crowded environments
Abstract
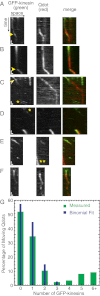
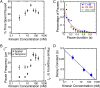
Intracellular transport of cargo particles is performed by multiple motors working in concert. However, the mechanism of motor association to cargos is unknown. It is also unknown how long individual motors stay attached, how many are active, and how multimotor cargos would navigate a densely crowded filament with many other motors. Prior theoretical and experimental biophysical model systems of intracellular cargo have assumed fixed teams of motors transporting along bare microtubules or microtubules with fixed obstacles. Here, we investigate a regime of cargos transporting along microtubules crowded with free motors. Furthermore, we use cargos that are able to associate or dissociate motors as it translocates. We perform in vitro motility reconstitution experiments with high-resolution particle tracking. Our model system consists of a quantum dot cargo attached to kinesin motors, and additional free kinesin motors that act as traffic along the microtubule. Although high densities of kinesin motors hinder forward motion, resulting in a lower velocity, the ability to associate motors appears to enhance the run length and attachment time of the quantum dot, improving overall cargo transport. These results suggest that cargos that can associate new motors as they transport could overcome traffic jams.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
How molecular motors are arranged on a cargo is important for vesicular transport.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 May;7(5):e1002032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002032. Epub 2011 May 5. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21573204 Free PMC article.
-
Processive movement of single kinesins on crowded microtubules visualized using quantum dots.EMBO J. 2006 Jan 25;25(2):267-77. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600937. Epub 2006 Jan 12. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16407972 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling intracellular transport in crowded environments: effects of motor association to cargos.Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2024 Jul 13;47(7):47. doi: 10.1140/epje/s10189-024-00440-9. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2024. PMID: 39002103
-
Hither and yon: a review of bi-directional microtubule-based transport.Phys Biol. 2004 Jun;1(1-2):R1-11. doi: 10.1088/1478-3967/1/2/R01. Phys Biol. 2004. PMID: 16204815 Review.
-
Bidirectional transport of organelles: unity and struggle of opposing motors.Cell Biol Int. 2012 Jan;36(1):1-6. doi: 10.1042/CBI20110413. Cell Biol Int. 2012. PMID: 22142363 Review.
Cited by
-
The crowding dynamics of the motor protein kinesin-II.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 13;15(2):e0228930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228930. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32053680 Free PMC article.
-
The Dark Matter of Biology.Biophys J. 2016 Sep 6;111(5):909-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.07.037. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27602719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simulation of receptor triggering by kinetic segregation shows role of oligomers and close contacts.Biophys J. 2022 May 3;121(9):1660-1674. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.03.033. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35367423 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin-2 KIF3AC and KIF3AB Can Drive Long-Range Transport along Microtubules.Biophys J. 2015 Oct 6;109(7):1472-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.08.004. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26445448 Free PMC article.
-
A fluid membrane enhances the velocity of cargo transport by small teams of kinesin-1.J Chem Phys. 2018 Mar 28;148(12):123318. doi: 10.1063/1.5006806. J Chem Phys. 2018. PMID: 29604873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caviston JP, Holzbaur EL. Microtubule motors at the intersection of trafficking and transport. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16(10):530–537. - PubMed
-
- Chevalier-Larsen E, Holzbaur EL. Axonal transport and neurodegenerative disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1762(11–12):1094–1108. - PubMed
-
- Hammond JW, Griffin K, Jih GT, Stuckey J, Verhey KJ. Co-operative versus independent transport of different cargoes by Kinesin-1. Traffic. 2008;9(5):725–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

