Identification and elimination of an immunodominant T-cell epitope in recombinant immunotoxins based on Pseudomonas exotoxin A
- PMID: 23213206
- PMCID: PMC3529021
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1218138109
Identification and elimination of an immunodominant T-cell epitope in recombinant immunotoxins based on Pseudomonas exotoxin A
Abstract
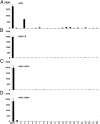
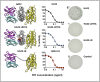
Recombinant immunotoxins (RITs) are chimeric proteins that are being developed for cancer treatment. We have produced RITs that contain PE38, a portion of the bacterial protein Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Because the toxin is bacterial, it often induces neutralizing antibodies, which limit the number of treatment cycles and the effectiveness of the therapy. Because T cells are essential for antibody responses to proteins, we adopted an assay to map the CD4(+) T-cell epitopes in PE38. We incubated peripheral blood mononuclear cells with an immunotoxin to stimulate T-cell expansion, followed by exposure to overlapping peptide fragments of PE38 and an IL-2 ELISpot assay to measure responses. Our observation of T-cell responses in 50 of 50 individuals correlates with the frequency of antibody formation in patients with normal immune systems. We found a single, highly immunodominant epitope in 46% (23/50) of the donors. The immunodominant epitope is DRB1-restricted and was observed in subjects with different HLA alleles, indicating promiscuity. We identified two amino acids that, when deleted or mutated to alanine, eliminated the immunodominant epitope, and we used this information to construct mutant RITs that are highly cytotoxic and do not stimulate T-cell responses in many donors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity of therapeutic recombinant immunotoxins.Immunol Rev. 2016 Mar;270(1):152-64. doi: 10.1111/imr.12390. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26864110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the B cell epitopes associated with a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE38) used to make immunotoxins for the treatment of cancer patients.J Immunol. 2006 Dec 15;177(12):8822-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.12.8822. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17142785
-
Identification of epitopes on a mutant form of Pseudomonas exotoxin using serum from humans treated with Pseudomonas exotoxin containing immunotoxins.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Jun;27(6):1459-68. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270624. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9209499 Clinical Trial.
-
Recombinant immunotoxin for cancer treatment with low immunogenicity by identification and silencing of human T-cell epitopes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 10;111(23):8571-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405153111. Epub 2014 May 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24799704 Free PMC article.
-
A guide to taming a toxin--recombinant immunotoxins constructed from Pseudomonas exotoxin A for the treatment of cancer.FEBS J. 2011 Dec;278(23):4683-700. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08182.x. Epub 2011 Jun 2. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21585657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paclitaxel synergizes with exposure time adjusted CD22-targeting immunotoxins against B-cell malignancies.Oncotarget. 2017 May 9;8(19):30644-30655. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16141. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423727 Free PMC article.
-
GPI-AP: Unraveling a New Class of Malignancy Mediators and Potential Immunotherapy Targets.Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 4;10:537311. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.537311. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33344222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Domain II of Pseudomonas Exotoxin Is Critical for Efficacy of Bolus Doses in a Xenograft Model of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 21;10(5):210. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050210. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29883379 Free PMC article.
-
Removing T-cell epitopes with computational protein design.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 10;111(23):8577-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321126111. Epub 2014 May 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24843166 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the Immunogenicity of the Cargo and of the Targeting Antibodies with a Focus on Demmunized Bacterial Toxins and on Antibody-Targeted Human Effector Proteins.Biomedicines. 2017 Jun 2;5(2):28. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines5020028. Biomedicines. 2017. PMID: 28574434 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hassan R, et al. Phase I study of SS1P, a recombinant anti-mesothelin immunotoxin given as a bolus I.V. infusion to patients with mesothelin-expressing mesothelioma, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(17):5144–5149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

