Direct and immune mediated antibody targeting of ERBB receptors in a colorectal cancer cell-line panel
- PMID: 23213241
- PMCID: PMC3529069
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1218750110
Direct and immune mediated antibody targeting of ERBB receptors in a colorectal cancer cell-line panel
Abstract
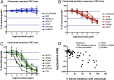
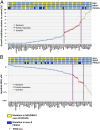
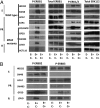
A significant proportion of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients are resistant to anti-ERBB1 [avian erythroblastic leukemia viral (v-erb-b) oncogene homolog, receptor for EGF] monoclonal antibodies (Mabs). We evaluated both immune and nonimmune effects of cetuximab (anti-ERBB1 Mab), trastuzumab (anti-ERBB2 Mab), pertuzumab (anti-ERBB2 Mab), and lapatinib (dual ERBB1 and ERBB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor) in a large well-characterized panel of 64 CRC cell lines to find response predictive tumor characteristics. There was a significant correlation between the direct effects of cetuximab and lapatinib. Both agents were associated (P = 0.0004) with "triple' wild-type status in KRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA exon 20. Most cell lines were resistant to the direct effects of anti-ERBB2 Mabs, suggesting that the effects of lapatinib might mainly be through ERBB1. Microarray mRNA expression profiles of sensitive and resistant cell lines showed that although ERBB1 receptor or ligand levels did not associate with cetuximab sensitivity, high levels of ERBB2 (P = 0.036) and amphiregulin (P = 0.026) predicted sensitivity to lapatinib. However, higher ERBB1 expression predicted susceptibility to cetuximab-induced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and occurred independently of KRAS/BRAF/PIK3CA mutations (P = 0.69). Lapatinib may be an effective alternative therapy to cetuximab in triple wild-type tumors. Microarray analysis provides suggestive biomarkers for resistance. ERBB1 levels, independent of mutation status, predict immune killing. Therefore, anti-ERBB1 antibodies may be considered in CRC tumors with higher ERBB1 expression and favorable FcγR polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
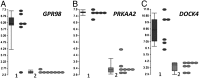
References
-
- Messersmith WA, Ahnen DJ. Targeting EGFR in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(17):1834–1836. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, et al. Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: Updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):2011–2019. - PubMed
-
- De Roock W, et al. KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, and PTEN mutations: Implications for targeted therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(6):594–603. - PubMed
-
- Walther A, et al. Genetic prognostic and predictive markers in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(7):489–499. - PubMed
-
- Carter PJ. Potent antibody therapeutics by design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(5):343–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

