Vitamin C Induces Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cell Line, HCT-8 Via the Modulation of Calcium Influx in Endoplasmic Reticulum and the Dissociation of Bad from 14-3-3β
- PMID: 23213312
- PMCID: PMC3509163
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2012.12.5.189
Vitamin C Induces Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cell Line, HCT-8 Via the Modulation of Calcium Influx in Endoplasmic Reticulum and the Dissociation of Bad from 14-3-3β
Abstract
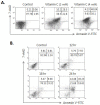
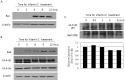
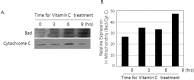
It has been reported that vitamin C plays an effective role in the treatment and prevention of cancer, but its specific mechanisms are still largely unknown. The incidence of colon cancer is now increasing in Korea. Therefore, we have examined here the effect of vitamin C on the induction of the apoptosis on colon cancer and its related mechanisms. We have found that remarkable increase of the apoptosis and the calcium influx in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in human colon cancer cell line, HCT-8. However, vitamin C-induced apoptosis was effectively inhibited by the pre-treatment of BAPTA-AM (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy) ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid), which is well-known as a calcium specific chelator. During the apoptosis, we found the increase of the translocation of Bad to mitochondria from cytosol, after releasing from 14-3-3β. In this process, the expression of Bax, a well-known pro-apoptotic protein, was also increased. Taken together, vitamin C induces apoptosis of colon cancer cell line, HCT-8 through the increase of 1) the calcium influx in endoplasmic reticulum (ER), 2) the translocation of Bad to mitochondria, and 3) the expression of Bax.
Keywords: 14-3-3β; Apoptosis; Bad; Colon cancer; Endoplasmic raticulum; Vitamin C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kang JS, Cho D, Kim YI, Hahm E, Kim YS, Jin SN, Kim HN, Kim D, Hur D, Park H, Hwang YI, Lee WJ. Sodium ascorbate (vitamin C) induces apoptosis in melanoma cells via the down-regulation of transferrin receptor dependent iron uptake. J Cell Physiol. 2005;204:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Kim JE, Jin DH, Lee SD, Hong SW, Shin JS, Lee SK, Jung DJ, Kang JS, Lee WJ. Vitamin C inhibits p53-induced replicative senescence through suppression of ROS production and p38 MAPK activity. Int J Mol Med. 2008;22:651–655. - PubMed
-
- Hahm E, Jin DH, Kang JS, Kim YI, Hong SW, Lee SK, Kim HN, Jung da J, Kim JE, Shin DH, Hwang YI, Kim YS, Hur DY, Yang Y, Cho D, Lee MS, Lee WJ. The molecular mechanisms of vitamin C on cell cycle regulation in B16F10 murine melanoma. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102:1002–1010. - PubMed
-
- Lee SK, Kang JS, Jung da J, Hur DY, Kim JE, Hahm E, Bae S, Kim HW, Kim D, Cho BJ, Cho D, Shin DH, Hwang YI, Lee WJ. Vitamin C suppresses proliferation of the human melanoma cell SK-MEL-2 through the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and the modulation of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) production. J Cell Physiol. 2008;216:180–188. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

