Mechanisms of action of topical corticosteroids in psoriasis
- PMID: 23213332
- PMCID: PMC3508578
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/561018
Mechanisms of action of topical corticosteroids in psoriasis
Abstract
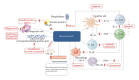
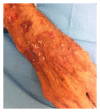
Psoriasis is a lifelong, chronic, and immune-mediated systemic disease, which affects approximately 1-3% of the Caucasian population. The different presentations of psoriasis require different approaches to treatment and appropriate prescriptions according to disease severity. The use of topical therapy remains a key component of the management of almost all psoriasis patients, and while mild disease is commonly treated only with topical agents, the use of topical therapy as adjuvant therapy in moderate-to-severe disease may also be helpful. This paper focuses on the cutaneous mechanisms of action of corticosteroids and on the currently available topical treatments, taking into account adverse effects, bioavailability, new combination treatments, and strategies to improve the safety of corticosteroids. It is established that the treatment choice should be tailored to match the individual patient's needs and his/her expectations, prescribing to each patient the most suitable vehicle.
Figures

References
-
- Saraceno R, Gramiccia T, Frascione P, Chimenti S. Calcipotriene/betamethasone in the treatment of psoriasis: a review article. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 2009;10(14):2357–2365. - PubMed
-
- Lowes MA, Bowcock AM, Krueger JG. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature. 2007;445(7130):866–873. - PubMed
-
- Laws PM, Young HS. Topical treatment of psoriasis. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 2010;11(12):1999–2009. - PubMed
-
- Henseler T, Christophers E. Psoriasis of early and late onset: characterization of two types of psoriasis vulgaris. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1985;13(3):450–456. - PubMed
-
- Lebwohl M. Psoriasis. The Lancet. 2003;361(9364):1197–1204. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

