Vitamins e and C alleviate the germ cell loss and oxidative stress in cryptorchidism when administered separately but not when combined in rats
- PMID: 23213563
- PMCID: PMC3503317
- DOI: 10.5402/2012/843569
Vitamins e and C alleviate the germ cell loss and oxidative stress in cryptorchidism when administered separately but not when combined in rats
Abstract
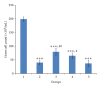
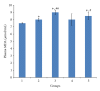
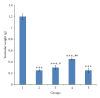
The antioxidant effects of vitamins C and E on cryptorchidism-induced oxidative stress were investigated in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Forty rats (200-250 g) were randomly divided in a blinded fashion into five groups (n = 8). Group 1 was sham operated and treated with vehicle (corn-oil, 10 mL/kg). Groups 2, 3, 4, and 5 were rendered unilaterally cryptorchid and treated with vehicle (10 mL/kg), vitamin E solution (75 mg/kg), vitamin C solution (1.25 g/kg), and combination of vitamin E (75 mg/kg) and vitamin C (1.25 g/kg) solutions, respectively. Germ cell count, superoxide dismutase (SOD), total protein (TP), and testicular weight (TW) were lower, but malondialdhyde (MDA) was higher in the cryptorchid rats than the sham-operated rats. When administered separately, vitamins C and E increased germ cell count, SOD, TP, and TW but did not reduce MDA in the cryptorchid rats when compared to the vehicle-treated cryptorchid rats. However, there was no significant difference in these parameters between vehicle-treated and combined vitamins C- and E-treated rats. This suggests that vitamins E and C alleviate the germ cell loss and oxidative stress in cryptorchidism when administered separately but not when combined in rats.
Figures


References
-
- Fairfield KM, Fletcher RH. Vitamins for chronic disease prevention in adults: scientific review. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2002;287(23):3116–3126. - PubMed
-
- Polidori MC, Mecocci P, Browne SE, Senin U, Beal MF. Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA in Huntington's disease parietal cortex. Neuroscience Letters. 1999;272(1):53–56. - PubMed
-
- Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Willett WC. Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary disease in women. New England Journal of Medicine. 1993;328(20):1444–1449. - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Oe T, Blair IA. Vitamin C-induced decomposition of lipid hydroperoxides to endogenous genotoxins. Science. 2001;292(5524):2083–2086. - PubMed
-
- Halliwell B. Vitamin C: poison, prophylactic or panacea? Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 1999;24(7):255–259. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
