Duplication of the external auditory canal: two cases and a review of the literature
- PMID: 23213587
- PMCID: PMC3507044
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/924571
Duplication of the external auditory canal: two cases and a review of the literature
Abstract
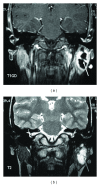
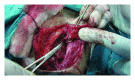
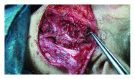
The objective of the present paper is to describe the clinical presentation, diagnostic process, surgical treatment, and outcome of 2 patients with first branchial cleft anomaly. The first case was an 8-year-old girl presented with an elastic lesion located in the left infra-auricular area, in close relation with the lobule, duplicating the external auditory canal. The magnetic resonance imaging revealed a lesion, appearing as a rather well-circumscribed mass within the left parotid gland and duplicating the ear canal. A superficial parotidectomy was subsequently performed, with total excision of the cyst. The second patient was a 15-year-old girl presented with a congenital fistula of the right lateral neck. At superficial parotidectomy, a total excision of the fistula was performed. During the operation the tract was recorded to lay between the branches of the facial nerve, extending with a blind ending canal parallel to the external acoustic meatus. Conclusively, first branchial cleft anomalies are rare malformations with cervical, parotid, or auricular clinical manifestations. Diagnosis of first branchial cleft lesions is achieved mainly through careful physical examination. Complete surgical excision with wide exposure of the lesion is essential in order to achieve permanent cure and avoid recurrence.
Figures



References
-
- Olsen KD, Maragos NE, Weiland LH. First branchial cleft anomalies. Laryngoscope. 1980;90(3):423–436. - PubMed
-
- D’Souza AR, Uppal HS, De R, Zeitoun H. Updating concepts of first branchial cleft defects: a literature review. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 2002;62(2):103–109. - PubMed
-
- Ford GR, Balakrishnan A, Evans JNG, Bailey CM. Branchial cleft and pouch anomalies. Journal of Laryngology and Otology. 1992;106(2):137–143. - PubMed
-
- Mukherji SK, Tart RP, Slattery WH, Stringer SP, Benson MT, Mancuso AA. Evaluation of first branchial anomalies by CT and MR. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 1993;17(4):576–581. - PubMed
-
- Benson MT, Dalen K, Mancuso AA, Kerr HH, Cacciarelli AA, Mafee MF. Congenital anomalies of the branchial apparatus: embryology and pathologic anatomy. Radiographics. 1992;12(5):943–960. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

