Continuous and Long-Term Measurement of Reticuloruminal pH in Grazing Dairy Cows by an Indwelling and Wireless Data Transmitting Unit
- PMID: 23213627
- PMCID: PMC3504470
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/236956
Continuous and Long-Term Measurement of Reticuloruminal pH in Grazing Dairy Cows by an Indwelling and Wireless Data Transmitting Unit
Abstract
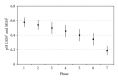
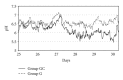
The aim of the present study was the continuous measurement of ruminal pH in grazing dairy cows to monitor the diets effects on ruminal pH value. A novel indwelling pH-measurement and data transmitting system was given to 6 multiparous cows orally. Ruminal pH was measured every 600 sec over a 40 d period. After barn feeding and changeover to pasture, the following 3 treatments (2 cows/treatment) were included in the measurement period: continuous grazing (G), continuous grazing plus 4 kg/d of hay fed twice daily (GH), and continuous grazing plus 4 kg/d of concentrate (GC). Ruminal pH decreased significantly (P < 0.05) from 6.58 ± 0.15 to pH 6.19 ± 0.19 during feed changeover to pasture. Mean ruminal pH for G, GH, and GC was 6.36, 6.56, and 6.01. Mean 24-h minimum pH was 5.95, 6.20 and, 5.58. The time pH was below 6.3, 6.0, 5.8, and 5.5, for G it was 583, 91, 26, and 3 min/d, for GH it was 97, 12, 0, and 0 min/d and for GC it was 1126, 621, 347, and 101 min/d, respectively. Results were significantly influenced by the diet. The indwelling pH-measurement and data transmitting system is a very useful and proper tool for long-term measurement of ruminal pH in cows.
Figures
References
-
- Duffield T, Plaizier JC, Fairfield A, et al. Comparison of techniques for measurement of rumen pH in lactating dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science. 2004;87(1):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Bramley E, Lean IJ, Fulkerson WJ, Stevenson MA, Rabiee AR, Costa ND. The definition of acidosis in dairy herds predominantly fed on pasture and concentrates. Journal of Dairy Science. 2008;91(1):308–321. - PubMed
-
- O’Grady L, Doherty ML, Mulligan FJ. Subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) in grazing Irish dairy cows. Veterinary Journal. 2008;176(1):44–49. - PubMed
-
- Gasteiner J. Grundlagen zu den Verdauungsvorgängen beim Rind (Anatomie, Physiologie, Mikroflora) Bericht Zur Viehwirtschaftlichen Fachtagung. 2001;28:69–75.
-
- Enemark JMD. The monitoring, prevention and treatment of sub-acute ruminal acidosis (SARA): a review. Veterinary Journal. 2008;176(1):32–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

