On the formation and properties of interstrand DNA-DNA cross-links forged by reaction of an abasic site with the opposing guanine residue of 5'-CAp sequences in duplex DNA
- PMID: 23215239
- PMCID: PMC4012394
- DOI: 10.1021/ja308119q
On the formation and properties of interstrand DNA-DNA cross-links forged by reaction of an abasic site with the opposing guanine residue of 5'-CAp sequences in duplex DNA
Abstract
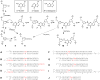
We recently reported that the aldehyde residue of an abasic (Ap) site in duplex DNA can generate an interstrand cross-link via reaction with a guanine residue on the opposing strand. This finding is intriguing because the highly deleterious nature of interstrand cross-links suggests that even small amounts of Ap-derived cross-links could make a significant contribution to the biological consequences stemming from the generation of Ap sites in cellular DNA. Incubation of 21-bp duplexes containing a central 5'-CAp sequence under conditions of reductive amination (NaCNBH(3), pH 5.2) generated much higher yields of cross-linked DNA than reported previously. At pH 7, in the absence of reducing agents, these Ap-containing duplexes also produced cross-linked duplexes that were readily detected on denaturing polyacrylamide gels. Cross-link formation was not highly sensitive to reaction conditions, and the cross-link, once formed, was stable to a variety of workup conditions. Results of multiple experiments including MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, gel mobility, methoxyamine capping of the Ap aldehyde, inosine-for-guanine replacement, hydroxyl radical footprinting, and LC-MS/MS were consistent with a cross-linking mechanism involving reversible reaction of the Ap aldehyde residue with the N(2)-amino group of the opposing guanine residue in 5'-CAp sequences to generate hemiaminal, imine, or cyclic hemiaminal cross-links (7-10) that were irreversibly converted under conditions of reductive amination (NaCNBH(3)/pH 5.2) to a stable amine linkage. Further support for the importance of the exocyclic N(2)-amino group in this reaction was provided by an experiment showing that installation of a 2-aminopurine-thymine base pair at the cross-linking site produced high yields (15-30%) of a cross-linked duplex at neutral pH, in the absence of NaCNBH(3).
Figures








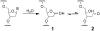

Similar articles
-
Interstrand Cross-Link Formation Involving Reaction of a Mispaired Cytosine Residue with an Abasic Site in Duplex DNA.Chem Res Toxicol. 2021 Apr 19;34(4):1124-1132. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00004. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Chem Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33784065 Free PMC article.
-
Interstrand DNA Cross-Links Derived from Reaction of a 2-Aminopurine Residue with an Abasic Site.ACS Chem Biol. 2019 Jul 19;14(7):1481-1489. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00208. Epub 2019 Jul 1. ACS Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31259519 Free PMC article.
-
A New Cross-Link for an Old Cross-Linking Drug: The Nitrogen Mustard Anticancer Agent Mechlorethamine Generates Cross-Links Derived from Abasic Sites in Addition to the Expected Drug-Bridged Cross-Links.Biochemistry. 2016 Dec 20;55(50):7033-7041. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b01080. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27992994
-
Novel Processes Associated with the Repair of Interstrand Cross-Links Derived from Abasic Sites in Duplex DNA: Roles for the Base Excision Repair Glycosylase NEIL3 and the SRAP Protein HMCES.Chem Res Toxicol. 2024 Feb 19;37(2):199-207. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.3c00345. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Chem Res Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38198604 Review.
-
Preparation of interstrand cross-linked DNA oligonucleotide duplexes.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:421-37. doi: 10.2741/1246. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766379 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical structure and properties of interstrand cross-links formed by reaction of guanine residues with abasic sites in duplex DNA.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Mar 25;137(11):3933-45. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00669. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25710271 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of cross-linked DNA containing oxidized abasic site analogues.J Org Chem. 2014 Jul 3;79(13):5948-57. doi: 10.1021/jo500944g. Epub 2014 Jun 20. J Org Chem. 2014. PMID: 24949656 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Purification of Oligodeoxynucleotide Duplexes Containing a Site-Specific, Reduced, Chemically Stable Covalent Interstrand Cross-Link Between a Guanine Residue and an Abasic Site.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1973:163-175. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9216-4_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31016701 Free PMC article.
-
Reconsidering the Chemical Nature of Strand Breaks Derived from Abasic Sites in Cellular DNA: Evidence for 3'-Glutathionylation.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Jun 15;144(23):10471-10482. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c02703. Epub 2022 May 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 35612610 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagenic Bypass of an Oxidized Abasic Lesion-Induced DNA Interstrand Cross-Link Analogue by Human Translesion Synthesis DNA Polymerases.Biochemistry. 2015 Dec 22;54(50):7409-22. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01027. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Biochemistry. 2015. PMID: 26626537 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

