Relationship between financial impact and coverage of drugs in Australia
- PMID: 23217275
- PMCID: PMC3582189
- DOI: 10.1017/S0266462312000724
Relationship between financial impact and coverage of drugs in Australia
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to estimate the relationship between the financial impact of a new drug and the recommendation for reimbursement by the Australian Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee (PBAC).
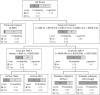
Methods: Data in the PBAC summary database were abstracted for decisions made between July 2005 and November 2009. Financial impact-the upper bound of the values presented in the PBAC summary database-was categorized as ≤A$0, >A$0 up to A$10 million, A$10 million up to A$30 million, and >A$30 million per year. Descriptive, logistic, survival, and recursive partitioning decision analyses were used to estimate the relationship between the financial impact of a new drug indication and the recommendation for reimbursement. Multivariable analyses controlled for other clinical and economic variables, including cost per quality-adjusted life-year gained.
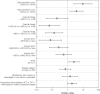
Results: Financial impact was a significant predictor of the recommendation for reimbursement. In the logistic analysis, the odds ratios of reimbursement for drug submissions with financial impacts ≥A$10 million to ≥A$30 million or >A$0 to <A$10 million compared with ≤A$0 were 0.12 (95 percent confidence interval [CI]: 0.03-0.51) and 0.16 (95 percent CI: 0.04-0.60), respectively. In the recursive partition decision analysis, the first split of the data was for submissions with a positive financial impact compared with those with a zero or negative financial impact.
Conclusions: In Australia, financial impact on the drug budget is an important determinant of whether a new drug is recommended for reimbursement when cost-effectiveness estimates and other clinical and economic variables are controlled.
Figures

References
-
- Haute Autorité de Santé (HAS), College des Economistes de la Sante. French guidelines for the economic evaluation of health care technologies. 2004. [cited 2010 October 18]. Available from: http://www.ispor.org/peguidelines/source/France_Guidelines_HE_Evaluation...
-
- Institut für Qualität und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesundheitswesen (Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care) (IQWiG). IQWiG methods for assessment of the relation of benefits to costs in the German statutory health care system, version 1.1. 2008. [cited 2010 October 18]. Available from: http://www.iqwig.de/download/08-01-24_Draft_Methods_of_the_Relation_of_B... - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) Single technology appraisal specification for manufacturer/sponsor submission of evidence. 2009. [cited 2010 October 18]. Available from: http://www.nice.org.uk/media/E29/DF/SpecificationForManufacturerSponsorS...
-
- Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee (PBAC) Guidelines for preparing submissions to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee, version 4.2. 2007. [cited 2010 October 18]. Available from: http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/pbacguidel...
-
- WellPoint Health technology assessment guidelines. 2008. [cited 2010 October 18]. Available from: https://www.wellpointnextrx.com/shared/noapplication/f1/s0/t0/pw_ad08061...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

