The harmonies played by TGF-β in stem cell biology
- PMID: 23217421
- PMCID: PMC3612991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.11.001
The harmonies played by TGF-β in stem cell biology
Abstract
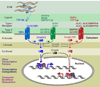
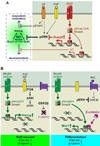
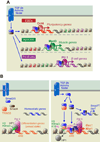
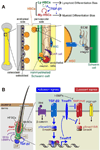
To rejuvenate tissues and/or repair wounds, stem cells must receive extrinsic signals from their surrounding environment and integrate them with their intrinsic abilities to self-renew and differentiate to make tissues. Increasing evidence suggests that the superfamily of transforming growth factor-βs (TGF-βs) constitute integral components in the intercellular crosstalk between stem cells and their microenvironment. In this review, we summarize recent advances in our understanding of TGF-β superfamily functions in embryonic and adult stem cells. We discuss how these pathways help to define the physiological environment where stem cells reside, and how perturbations in the signaling circuitry contribute to cancers.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Agricola E, Randall RA, Gaarenstroom T, Dupont S, Hill CS. Recruitment of TIF1γ to chromatin via its PHD finger-bromodomain activates its ubiquitin ligase and transcriptional repressor activities. Mol Cell. 2011;43:85–96. - PubMed
-
- Akhurst RJ. Large- and small-molecule inhibitors of transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;7:513–521. - PubMed
-
- Annes JP, Munger JS, Rifkin DB. Making sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Arnold SJ, Robertson EJ. Making a commitment: cell lineage allocation and axis patterning in the early mouse embryo. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:91–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

