Anti-viral CD8 T cells and the cytokines that they love
- PMID: 23217625
- PMCID: PMC3580945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.09.012
Anti-viral CD8 T cells and the cytokines that they love
Abstract
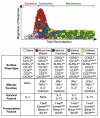
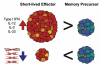
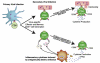
Viral infections cause an immunological disequilibrium that provokes CD8 T cell responses. These cells play critical roles in purging acute infections, limiting persistent infections, and conferring life-long protective immunity. At every stage of the response anti-viral CD8 T cells are sensitive to signals from cytokines. Initially cytokines operate as immunological warning signs that inform of the presence of an infection, and also influence the developmental choices of the responding cells. Later during the course of the response other sets of cytokines support the survival and maintenance of the differentiated anti-viral CD8 T cells. Although many cytokines promote virus-specific CD8 T cells, other cytokines can suppress their activities and thus favor viral persistence. In this review we discuss how select cytokines act to regulate anti-viral CD8 T cells throughout the response and influence the outcome of viral infections.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Allard EL, Hardy MP, Leignadier J, Marquis M, Rooney J, Lehoux D, Labrecque N. Overexpression of IL-21 promotes massive CD8 memory T cell accumulation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007;37:3069–3077. - PubMed
-
- Aoshi T, Koyama S, Kobiyama K, Akira S, Ishii KJ. Innate and adaptive immune responses to viral infection and vaccination. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011;1:226–232. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann MF, Wolint P, Schwarz K, Jager P, Oxenius A. Functional properties and lineage relationship of CD8+ T cell subsets identified by expression of IL-7 receptor alpha and CD62L. J. Immunol. 2005;175:4686–4696. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann MF, Wolint P, Walton S, Schwarz K, Oxenius A. Differential role of IL-2R signaling for CD8+ T cell responses in acute and chronic viral infections. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007;37:1502–1512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

