Optimization of the reconstruction interval in neurovascular 4D-CTA imaging. A technical note
- PMID: 23217631
- PMCID: PMC3520550
- DOI: 10.1177/159101991201800402
Optimization of the reconstruction interval in neurovascular 4D-CTA imaging. A technical note
Abstract
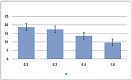
Time resolved whole brain CT angiography (4D-CTA) is a novel imaging technology providing information regarding blood flow. One of the factors that influence the diagnostic value of this examination is the temporal resolution, which is affected by the gantry rotation speed during acquisition and the reconstruction interval during post-processing. Post-processing determines the time spacing between two reconstructed volumes and, unlike rotation speed, does not affect radiation burden. The data sets of six patients who underwent a cranial 4D-CTA were used for this study. Raw data was acquired using a 320-slice scanner with a rotation speed of 2 Hz. The arterial to venous passage of an intravenous contrast bolus was captured during a 15 s continuous scan. The raw data was reconstructed using four different reconstruction-intervals: 0.2, 0.3, 0.5 and 1.0 s. The results were rated by two observers using a standardized score sheet. The appearance of each lesion was rated correctly in all readings. Scoring for quality of temporal resolution revealed a stepwise improvement from the 1.0 s interval to the 0.3 s interval, while no discernable improvement was noted between the 0.3 s and 0.2 s interval. An increase in temporal resolution may improve the diagnostic quality of cranial 4D-CTA. Using a rotation speed of 0.5 s, the optimal reconstruction interval appears to be 0.3 s, beyond which, changes can no longer be discerned.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High sensitivity and specificity of 4D-CTA in the detection of cranial arteriovenous shunts.Eur Radiol. 2019 Nov;29(11):5961-5970. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06234-4. Epub 2019 May 14. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31089848 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and classification of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas using 4D-CT angiography: initial experience.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011 Jan;32(1):49-53. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2248. Epub 2010 Oct 21. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 20966056 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved 3D rotational angiography: display of detailed neurovascular anatomy in patients with intracranial vascular malformations.J Neurointerv Surg. 2017 Sep;9(9):887-894. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012462. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017. PMID: 27492375
-
Is four-dimensional CT angiography as effective as digital subtraction angiography in the detection of the underlying causes of intracerebral haemorrhage: a systematic review.Neuroradiology. 2020 Mar;62(3):273-281. doi: 10.1007/s00234-019-02349-z. Epub 2020 Jan 4. Neuroradiology. 2020. PMID: 31901972 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic imaging of cerebrovascular disease on multi-detector row computed tomography (MDCT)].Brain Nerve. 2011 Sep;63(9):923-32. Brain Nerve. 2011. PMID: 21878694 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
4D-CTA in neurovascular disease: a review.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015 Jun;36(6):1026-33. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4162. Epub 2014 Oct 29. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 25355812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow diversion in the treatment of carotid injury and carotid-cavernous fistula after transsphenoidal surgery.Interv Neuroradiol. 2015 Jun;21(3):346-50. doi: 10.1177/1591019915582367. Epub 2015 May 26. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 26015526 Free PMC article.
-
Arteriovenous Malformations Treated With Frameless Robotic Radiosurgery Using Non-Invasive Angiography: Long-Term Outcomes of a Single Center Pilot Study.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 30;10:570782. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.570782. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33330045 Free PMC article.
-
High sensitivity and specificity of 4D-CTA in the detection of cranial arteriovenous shunts.Eur Radiol. 2019 Nov;29(11):5961-5970. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06234-4. Epub 2019 May 14. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31089848 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation Dose Reduction in 4D Cerebral CT Angiography by Individualized Estimation of Cerebral Circulation Time.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 Dec;37(12):2189-2194. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4911. Epub 2016 Aug 25. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 27561832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siebert E, Bohner G, Masuhr F, et al. Neuroimaging by 320-row CT: is there a diagnostic benefit or is it just another scanner? A retrospective evaluation of 60 consecutive acute neurological patients. Neurological Sci. 2010;31:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Siebert E, Bohner G, Dewey M, et al. 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation. Br J Radiol. 2009;82:561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

