CYP1B1, MYOC, and LTBP2 mutations in primary congenital glaucoma patients in the United States
- PMID: 23218701
- PMCID: PMC3736560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2012.09.012
CYP1B1, MYOC, and LTBP2 mutations in primary congenital glaucoma patients in the United States
Abstract
Purpose: To screen primary congenital glaucoma patients in the United States for sequence variants within the CYP1B1, LTBP2, and MYOC genes using Sanger and whole exome sequencing.
Design: Retrospective case-control study.
Methods: Fifty-seven primary congenital glaucoma patients (47 families), 71 unaffected family members of the primary congenital glaucoma probands, and 101 healthy unrelated individuals were recruited from a single institution. Sanger sequencing of the primary congenital glaucoma gene, CYP1B1, was performed on 47 proband deoxyribonucleic acid samples. Simultaneously, whole exome sequencing was conducted on 3 families, each including more than 1 affected individual. Concurrently, 33 of 47 primary congenital glaucoma probands with extended family deoxyribonucleic acid samples were screened for LTBP2 and MYOC gene mutations. Exome-sequenced variations were validated by additional Sanger sequencing to confirm segregation of filtered disease-causing single nucleotide variations.
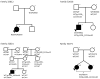
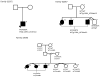
Results: Seven primary congenital glaucoma families (14.9%) manifested disease phenotypes attributable to CYP1B1 mutations. One primary congenital glaucoma family possessed homozygous mutant alleles, whereas 6 families carried compound heterozygous mutations. Five novel combinations of compound heterozygous mutations were identified, of which 2 combinations were found with whole exome sequencing. No disease-causing mutations within the LTBP2 and MYOC genes were discovered.
Conclusions: This study analyzed CYP1B1, LTBP2, and MYOC mutations in a cohort of primary congenital glaucoma patients from the United States, applying whole exome sequencing as a complementary tool to Sanger sequencing. Whole exome sequencing, coupled with Sanger sequencing, may identify novel genes in primary congenital glaucoma patients who have no mutations in known primary congenital glaucoma genes.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the icmje form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and none were reported.
Figures
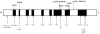
References
-
- Allingham RR, Freedman S, Shields MB. Shields’ Textbook of Glaucoma. 5. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. pp. 235–251.
-
- Abu-Amero KK, Edward DP. Primary congenital glaucoma. In: Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Stephens K, Adam MP, editors. GeneReviews. Seattle: University of Washington; Sep 30, 2004. [Accessed February 10, 2012]. last revision August 25, 2011. Available at: www.ncbi.nih.gov/books/NBK1135.
-
- Dimasi DP, Hewitt AW, Straga T, et al. Prevalence of CYP1B1 mutations in Australian patients with primary congenital glaucoma. Clin Genet. 2007;72(3):255–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

