Comparative effectiveness of maxillomandibular advancement and uvulopalatopharyngoplasty for the treatment of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 23219145
- PMCID: PMC3604163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2012.10.003
Comparative effectiveness of maxillomandibular advancement and uvulopalatopharyngoplasty for the treatment of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Purpose: To directly compare the clinical effectiveness of maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) and uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)--performed alone and in combination--for the treatment of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Patients and methods: The investigators designed and implemented a retrospective cohort study composed of patients with moderate to severe OSA (baseline AHI >15). The predictor variable was operative treatment and included MMA, UPPP, and UPPP followed by MMA (UPPP/MMA). The primary outcome variable was the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) measured preoperatively and 3 months to 6 months postoperatively. Other variables were grouped into the following categories: demographic, respiratory, and sleep parameters. Descriptive and bivariate statistics were computed.
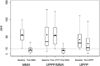
Results: The sample was composed of 106 patients grouped as follows: MMA (n = 37), UPPP (n = 34), and UPPP/MMA (n = 35) for treatment of OSA. There were no significant differences between the 3 groups for the study variables at baseline, except for AHI. Surgical treatment resulted in a significant decrease in AHI in each group: MMA (baseline AHI, 56.3 ± 22.6 vs AHI after MMA, 11.4 ± 9.8; P < .0001), UPPP/MMA (baseline AHI, 55.7 ± 49.2 vs AHI after UPPP/MMA, 11.6 ± 10.7; P < .0001), and UPPP (baseline AHI, 41.8 ± 28.0 vs AHI after UPPP, 30.1 ± 27.5; P = .0057). After adjusting for differences in baseline AHI, the estimated mean change in AHI was significantly larger for MMA compared with UPPP (MMA AHI, -40.5 vs UPPP AHI, -19.4; P = < .0001). UPPP/MMA was no more effective than MMA (P = .684).
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that MMA should be the surgical treatment option of choice for most patients with moderate to severe OSA who are unable to adequately adhere to CPAP.
Copyright © 2013 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK, Shahar E, Samet JM, Redline S, D'Agostino RB, Newman AB, Lebowitz MD, Pickering TG. Association of sleep-disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep Heart Health Study. JAMA. 2000;283:1829. - PubMed
-
- Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J. Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1378. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Peppard P, Palta M, Hla KM, Finn L, Morgan B, Skatrud J. Population-based study of sleep-disordered breathing as a risk factor for hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:1746. - PubMed
-
- Punjabi NM, Shahar E, Redline S, Gottlieb DJ, Givelber R, Resnick HE. Sleep-disordered breathing, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;160:521. - PubMed
-
- Shahar E, Whitney CW, Redline S, Lee ET, Newman AB, Javier Nieto F, O'Connor GT, Boland LL, Schwartz JE, Samet JM. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: cross-sectional results of the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources