Delayed administration of a PTEN inhibitor BPV improves functional recovery after experimental stroke
- PMID: 23219909
- PMCID: PMC3691271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.050
Delayed administration of a PTEN inhibitor BPV improves functional recovery after experimental stroke
Abstract
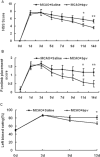
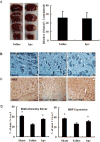
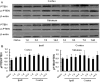
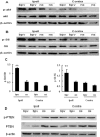
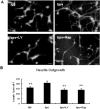
Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) inhibitors administered prior to or immediately after experimental stroke confer acute neuroprotection. However, it remains unclear if delayed treatment with a PTEN inhibitor improves long-term functional recovery after stroke. We addressed the issue in this study. Adult male mice were subjected to 1h of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) followed by treatment with a well-established PTEN inhibitor BPV or saline daily for 14 days, starting at 24h after MCAO. Functional recovery was assessed with behavioral tests and acute infarct volumes were analyzed histologically. Delayed BPV treatment did not reduce infarction during the acute phase, but significantly improved long-term functional recovery after MCAO. Since PTEN is a critical intrinsic inhibitory factor in axonal regeneration, we further examined BPV effects on axonal densities following MCAO using bielschowsky silver staining and immunohistochemistry with antibodies against myelin basic protein. Delayed BPV treatment significantly increased axon densities in the ischemic brain at 14 days after MCAO. Moreover, PTEN expression persistently remained high in the ischemic brain over 14 days after MCAO, and BPV treatment increased post-ischemic activation of Akt and mTOR in the ischemic brain. Akt and mTOR activation are the well-established cascades downstream to PTEN inhibition and have been shown to contribute to post-injury axonal regrowth in response to PTEN inhibition. Consistently, in an in vitro neuronal ischemia model, BPV enhanced axonal outgrowth of primary cortical neurons after oxygen-glucose deprivation and the enhancing effects were abolished by Akt/mTOR inhibition. In conclusion, delayed BPV treatment improved functional recovery from experimental stroke possibly via enhancing axonal growth and Akt/mTOR activation contributed to BPV-enhanced post-stroke axon growth.
Copyright © 2012 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M, Zhang X, Chopp M. Therapeutic benefit of intracerebral transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurol Sci. 2001a;189:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M, Willing AE, Sanchez-Ramos J, Chopp M. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke. 2001b;32:2682–2688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

