Predator odor-evoked BOLD activation in the awake rat: modulation by oxytocin and V₁a vasopressin receptor antagonists
- PMID: 23219972
- PMCID: PMC3809104
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.11.045
Predator odor-evoked BOLD activation in the awake rat: modulation by oxytocin and V₁a vasopressin receptor antagonists
Abstract
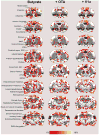
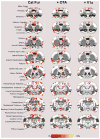
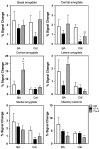
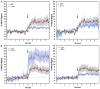
Modulators of unconditioned fear are potential targets for developing treatments for anxiety disorders. We used blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) MRI to investigate the pattern of brain activity during the presentation of a predator odor (cat fur) and a repulsive novel odor, butyric acid (BA), to awake rats. We further tested whether odor-evoked BOLD activation involved oxytocin (OT) and vasopressin V(1a) receptors. Animals were subdivided into groups either administered an intracerebroventricular injection of artificial cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), an OT receptor antagonist or a V(1a) antagonist (125 ng/10 μL each) 90 min before studies. BA odor evoked robust brain activation across olfactory, sensory, memory and limbic regions. The magnitude of BOLD activation across these regions was greater for BA than with cat fur. However, blockade of OT and V(1a) receptors differentially modulated odor evoked neural activity, particularly in the amygdala. OT and V(1a) antagonism preferentially modulated BOLD responding to BA in the cortical amygdala. While, OT and V(1a) antagonisms preferentially modulated BOLD responding to cat fur in the central amygdala. The data suggest that although OT receptors modulate BOLD activation in response to a novel and repulsive odor such as BA, vasopressin V(1a) receptors exert a modulatory influence on the neural response to a predator odor.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Appenrodt E, Schnabel R, Schwarzberg H. Vasopressin administration modulates anxiety-related behavior in rats. Physiol Behav. 1998;64:543–547. - PubMed
-
- Bielsky IF, Hu SB, Szegda KL, Westphal H, Young LJ. Profound impairment in social recognition and reduction in anxiety-like behavior in vasopressin V1a receptor knockout mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:483–493. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard DC, Markham C, Yang M, Hubbard D, Madarang E, Blanchard RJ. Failure to produce conditioning with low-dose trimethylthiazoline or cat feces as unconditioned stimuli. Behav Neurosci. 2003;117:360–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

