Retrodialysis of N/OFQ into the nucleus accumbens shell blocks cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine and locomotor activity
- PMID: 23219985
- PMCID: PMC3570659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.11.050
Retrodialysis of N/OFQ into the nucleus accumbens shell blocks cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine and locomotor activity
Abstract
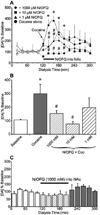
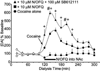
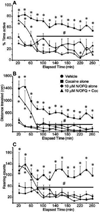
Nociceptin (N/OFQ) has been implicated in a variety of neurological disorders, most notably in reward processes and drug abuse. N/OFQ suppresses extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) after intracerebroventricular injection. This study sought to examine the effects of retrodialyzed N/OFQ on the cocaine-induced increase in extracellular dopamine levels in the NAc, as well as locomotor activity, in freely moving rats. 1.0μM, 10μM, and 1mM N/OFQ, in the NAc shell, significantly suppressed the cocaine-induced dopamine increase in the NAc, while N/OFQ alone had no significant effect on dopamine levels. Co-delivery of the selective NOP receptor antagonist SB612111 ([(-)-cis-1-Methyl-7-[[4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzocyclohepten-5-ol] reversed the N/OFQ suppression of cocaine-induced dopamine in the NAc, suggesting that this is an NOP receptor-mediated effect. Using a novel system to assess locomotion, we measured various motor activities of the animals with simultaneous microdialysis from the home cage. Cocaine produced an expected increase in total activity, including horizontal movement and rearing behavior. Retrodialysis of N/OFQ with cocaine administration affected all motor activities, initially showing no effect on behavior, but over time inhibiting cocaine-induced motor behaviors. These results suggest that N/OFQ can act directly in the NAc shell to block cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine levels. Extracellular dopamine and locomotor activity can be dissociated within the NAc and may reflect motor output differences in shell versus core regions of the NAc. These studies confirm the widespread involvement of NOP receptors in drug addiction and further validate the utility of an NOP receptor agonist as a medication for treatment of drug addiction.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orphanin FQ/nociceptin attenuates motor stimulation and changes in nucleus accumbens extracellular dopamine induced by cocaine in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001 Feb;154(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s002130000609. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11291998 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological characterization of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor antagonist SB-612111 [(-)-cis-1-methyl-7-[[4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzocyclohepten-5-ol]: in vitro studies.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jun;321(3):961-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.116764. Epub 2007 Feb 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17329552
-
Activation of nociceptin/orphanin FQ-NOP receptor system inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation, dopamine synthesis, and dopamine D(1) receptor signaling in rat nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum.J Neurochem. 2008 Oct;107(2):544-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05629.x. Epub 2008 Sep 18. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18717817
-
The nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor (NOP) as a target for drug abuse medications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(9):1151-6. doi: 10.2174/156802611795371341. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21050175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental and Adult Striatal Patterning of Nociceptin Ligand Marks Striosomal Population With Direct Dopamine Projections.J Comp Neurol. 2024 Dec;532(12):e70003. doi: 10.1002/cne.70003. J Comp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39656141 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of neurotransmitters in the action of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide-receptor system on passive avoidance learning in rats.Neurochem Res. 2014 Aug;39(8):1477-83. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1337-8. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24893797
-
The Nociceptin Receptor (NOP) Agonist AT-312 Blocks Acquisition of Morphine- and Cocaine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Mice.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Nov 29;9:638. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00638. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30555362 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic deletion or pharmacological blockade of nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptors in the ventral tegmental area attenuates nicotine-motivated behaviour.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;179(11):2647-2658. doi: 10.1111/bph.15762. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34854073 Free PMC article.
-
Does the kappa opioid receptor system contribute to pain aversion?Front Pharmacol. 2014 Nov 17;5:253. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00253. eCollection 2014. Front Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25452729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Specio SE, Khroyan TV, Neisewander JL. Effects of intraaccumbens administration of SCH-23390 on cocaine-induced locomotion and conditioned place preference. Synapse. 1998;30:181–193. - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, Khroyan TV, O'Dell LE, Fuchs RA, Neisewander JL. Differential effects of intra-accumbens sulpiride on cocaine-induced locomotion and conditioned place preference. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;279:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Barlocco D, Cignarella G, Giuseppe G, Grugn iM, Ronzoni S. In: Benzosuberonylpiperidine compounds as analgesics. GLAXOSMITHKLINE, editor. USA: GlaxoSmithKline S.p.A.; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

